8 辅助工具使用教程
备注
用DSPAW完成DFT计算后,想快速分析结果、画图,或者完成一些常见的数据处理任务?
dspawpy ( Python ≥ 3.9 )就是这样一款辅助工具,它可以编程调用(参考下文示例脚本),也提供了一个命令行交互程序
参考下方教程 安装 后,命令行输入 dspawpy 后回车即可使用交互程序:
... loading dspawpy cli ...
********这是dspawpy命令行交互小工具,预祝您使用愉快********
( )
_| | ___ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
/'_` |/',__)( '_`\ /'_` )( ) ( ) ( )( '_`\ ( ) ( )
( (_| |\__, \| (_) )( (_| || \_/ \_/ || (_) )| (_) |
\__,_)(____/| ,__/'`\__,_) \___x___/ | ,__/ \__, |
| | | | ( )_| |
(_) (_) \___/
[版本号]: [安装路径]
======================================
| 1: update更新
| 2: structure结构转化
| 3: volumetricData数据处理
| 4: band能带数据处理
| 5: dos态密度数据处理
| 6: bandDos能带和态密度共同显示
| 7: optical光学性质数据处理
| 8: neb过渡态计算数据处理
| 9: phonon声子计算数据处理
| 10: aimd分子动力学模拟数据处理
| 11: Polarization铁电极化数据处理
| 12: ZPE零点振动能数据处理
| 13: TS的热校正能
|
| q: 退出
======================================
--> 输入数字后回车选择功能:
亮点:
自动补全: 按Tab键即可生效,有助于快速且正确地输入程序所需要的参数
多线程懒加载:在等待用户输入时后台加载模块,大幅缩短等待时间;仅加载必要模块,减少内存占用
注意:
在远程服务器上使用时,由于机器的磁盘读写性能不佳,可能需要较长的启动时间,极端情况下可能长达半分钟(与服务器当时的磁盘读写性能直接相关)。如果无法忍受,请在自己的电脑上安装dspawpy使用
输入 dspawpy 回车后,python会先加载内建模块,完成后显示 ... loading dspawpy cli ... 提示语句,表明进入第二阶段(开始加载第三方依赖库)
等待第二阶段完成后,会显示欢迎界面,此时dspwapy已完成前期加载,进入第三阶段。后续将动态根据选择的功能模块加载相应的依赖库,从而最大限度减少等待时间
8.1 安装与更新
在HZW机器上,已提前安装 dspawpy,使用以下命令激活虚拟环境即可使用:
source /data/hzwtech/profile/dspawpy.env
在其他机器上,请自行安装 dspawpy(下列两种方式二选一):
使用 mamba 或 conda ,安装包可前往 https://conda-forge.org/download/ 下载
mamba install dspawpy -c conda-forge
#conda install dspawpy -c conda-forge
或使用 pip3 (部分操作系统中没有pip3可执行程序,此时请尝试pip)
pip3 install dspawpy
关于如何设置pip和conda镜像地址以加速安装过程,可参考 https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/pypi/ 和 https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/anaconda/
如果安装依然失败,请尝试上面的 mamba/conda 安装法。
警告
在集群上,由于权限问题,公共路径中的pip很可能不支持全局安装python库,必须在 pip install 后面追加 --user 选项安装到家目录 ~/.local/lib/python3.x/site-packages/ 下,其中3.x表示python解释器版本,x可能是9-13之间的任意整数
python将优先读取家目录下的dspawpy,即使公共环境中的dspawpy的版本比家目录中的dspawpy的版本新!
因此,如果以前用 --user 安装过dspawpy,又忘记手动更新家目录下的老版本dspawpy,即使source了公共环境,也无法调用公共环境中的dspawpy,依旧会使用老版本dspawpy,导致一些BUG。
因此,鉴于HZW集群每周自动更新dspawpy,建议不要在家目录下重复安装,已安装的建议删除 。如果在其他集群上,请确保及时手动更新家目录下的 dspawpy
如果不想删除家目录中的dspawpy,又不想更新它,可以在运行python脚本时,尝试 -s 选项避免导入家目录中的 dspawpy: python -s your-script.py。
更新 dspawpy
如果 dspawpy 是通过 mamba/conda 安装的,使用以下命令更新:
mamba update dspawpy
#conda update dspawpy
如果 dspawpy 是通过 pip 安装的,那么:
pip install dspawpy -U # -U 表示安装最新版
备注
如果 pip 使用了国内的镜像网站,可能由于镜像网站尚未同步最新版 dspawpy 而导致无法顺利升级,请使用如下命令告诉 pip 从pypi官网下载安装:
pip install dspawpy -i https://pypi.org/simple --user -U # -i 指定下载地址,--user 表示仅为当前用户安装,-U 表示安装最新版
如果运行时出现 dspawpy 相关 错误信息,请先检查是否已正确导入最新版本的 dspawpy 并检查安装路径:
$ python3 # 或 python
>>> import dspawpy
>>> dspawpy.__version__ # 将输出版本号
>>> dspawpy.__file__ # 将输出安装路径
8.2 structure结构转化
读取结构信息使用 read 函数;将结构信息写入文件,使用 write 函数;快速结构转化,使用 convert 函数:
可参考 2conversion.py 脚本完成转化:
1# coding:utf-8
2from dspawpy.io.structure import convert
3
4convert(
5 infile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.1/relax.h5", # Structure to be converted, if in the current path, you can just write the filename
6 si=None, # Select configuration number, if not specified, read all by default
7 ele=None, # Filter element symbol, default reads atomic information for all elements
8 ai=None, # Filter atomic indices, starting from 1, default to read all atomic information
9 infmt=None, # Input structure file type, e.g., 'h5'. If None, it will be matched ambiguously based on the filename rule.
10 task="relax", # Task type, this parameter is only valid when infile is a folder rather than a filename
11 outfile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/relaxed.xyz", # Structure file name
12 outfmt=None, # Output structure file type, e.g., 'xyz'. If None, it will be fuzzy matched according to filename rules.
13 coords_are_cartesian=True, # Written in Cartesian coordinates by default
14)
convert 函数的几个关键参数设置规则见下表:
infmt(输入文件格式) |
infile(输入文件名模糊匹配) |
outfmt(输出文件格式) |
outfile(输出文件名模糊匹配) |
说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
h5 |
*.h5 |
X |
X |
DS-PAW计算完成后保存的hdf5类型文件 |
json |
*.json |
json |
*.json |
DS-PAW计算完成后保存的json类型文件 |
pdb |
*.pdb |
pdb |
*.pdb |
Protein Data Bank |
as |
*.as |
as |
*.as |
DS-PAW记载原子坐标等信息的结构文件 |
hzw |
*.hzw |
hzw |
*.hzw |
DeviceStudio默认的结构文件 |
xyz |
*.xyz |
xyz |
*.xyz |
读取时仅支持分子结构的单构型,写入时则是包含晶胞的extended-xyz类型轨迹文件 |
X |
X |
dump |
*.dump |
lammps-dump类型轨迹文件 |
X |
*.cif*/*.mcif* |
cif/mcif |
*.cif*/*.mcif* |
Crystallographic Information File |
X |
*POSCAR*/*CONTCAR*/*.vasp/CHGCAR*/LOCPOT*/vasprun*.xml* |
poscar |
*POSCAR* |
VASP文件 |
X |
*.cssr* |
cssr |
*.cssr* |
Crystal Structure Standard Representation |
X |
*.yaml/*.yml |
yaml/yml |
*.yaml/*.yml |
YAML Ain't Markup Language |
X |
*.xsf* |
xsf |
*.xsf* |
eXtended Structural Format |
X |
*rndstr.in*/*lat.in*/*bestsqs* |
mcsqs |
*rndstr.in*/*lat.in*/*bestsqs* |
Monte Carlo Special Quasirandom Structure |
X |
inp*.xml/*.in*/inp_* |
fleur-inpgen |
*.in* |
FLEUR 结构文件,须额外安装 pymatgen-io-fleur 库 |
X |
*.res |
res |
*.res |
ShelX res 结构文件 |
X |
*.config*/*.pwmat* |
pwmat |
*.config/*.pwmat |
PWmat 文件 |
X |
X |
prismatic |
*prismatic* |
用于STEM模拟的一种文件格式 |
X |
CTRL* |
X |
X |
Stuttgart LMTO-ASA 文件 |
备注
上述表格中
*号表示任意字符,X表示不支持h5, json, pdb, xyz, dump, CONTCAR等格式支持多个结构组成的轨迹信息(常见于结构优化或者NEB或者AIMD任务)
in(out)fmt 参数优先级高于文件名模糊匹配规则;例如,指定 in(out)fmt='h5' 后,文件名可以是任意值,甚至可以是 a.json
将结构信息写为 json 格式时,仅支持可视化 NEB 链任务,详见 观察NEB链 节相关说明
DS-PAW 输出的 neb.h5、phonon.h5、phonon.json、neb.json以及wannier.json 暂时无法读取结构信息
8.3 volumetricData数据处理
volumetricData可视化
参考
3vis_vol.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.io.write import write_VESTA 3 4# Read data file (in h5 or json format), process it, and output to a cube file 5write_VESTA( 6 in_filename="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.2/rho.h5", # Path to the json or h5 file containing electronic system information 7 data_type="rho", # Data type, supported values are "rho", "potential", "elf", "pcharge", "rhoBound" 8 out_filename="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/DS-PAW_rho.cube", # Output file path 9 gridsize=(10, 10, 10), # Specifies the interpolation grid size 10 format="cube", # Supported formats: cube, vesta, and txt (xyz grid coordinates + values) 11)
将转换后的文件 DS-PAW_rho.cube 拖入 VESTA 软件中显示:
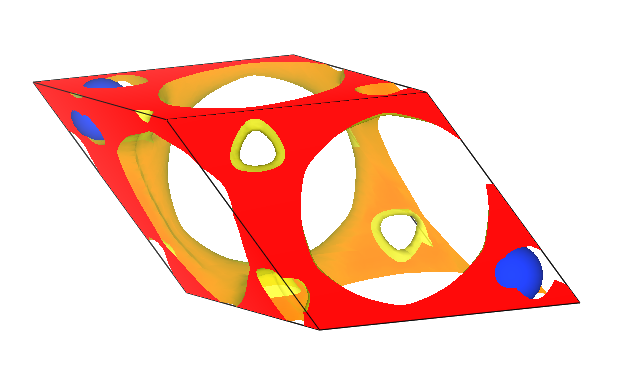
晶体硅单胞的电荷密度分布示意图
差分volumetricData可视化
参考
3dvol.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.io.write import write_delta_rho_vesta 3 4# Read the data file (h5 or json format), process it, and output it to a cube file, which can be directly opened with Vesta and has a small volume 5write_delta_rho_vesta( 6 total="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/supplement/AB.h5", # Data file for the system containing all components 7 individuals=[ 8 "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/supplement/A.h5", 9 "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/supplement/B.h5", 10 ], # Data files for the system containing each component 11 output="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/3delta_rho.cube", # Output file path 12)
上述脚本支持处理多元体系的电荷密度差,示例以二元体系为例,得到了 AB.h5 与 A.h5 和 B.h5 之间的电荷密度差文件 delta_rho.cube ,该文件可直接使用 VESTA 打开。
volumetricData面平均
参考
3planar_ave.py:
1# coding:utf-8
2from dspawpy.plot import average_along_axis
3
4axes = [
5 "2"
6] # "0", "1", "2" correspond to the x, y, z axes respectively; select which axes to average along
7axes_indices = [int(i) for i in axes]
8for ai in axes_indices:
9 plt = average_along_axis(
10 datafile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/3.3/scf.h5", # Data file path
11 task="potential", # Task name, can be 'rho', 'potential', 'elf', 'pcharge', 'rhoBound'
12 axis=ai, # Axis along which to plot the potential curve
13 smooth=False, # Whether to smooth
14 smooth_frac=0.8, # Smoothing coefficient
15 subtype=None, # Used to specify the subclass of task data, currently only used for Potential
16 label=f"axis{ai}", # Legend label
17 )
18if len(axes_indices) > 1:
19 plt.legend()
20
21plt.xlabel("Grid Index")
22plt.ylabel("TotalElectrostaticPotential (eV)")
23plt.savefig("dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/3pot_ave.png", dpi=300) # Image name
处理 应用案例 3.3 小节所得静电势文件,可得真空方向势函数曲线如下所示:
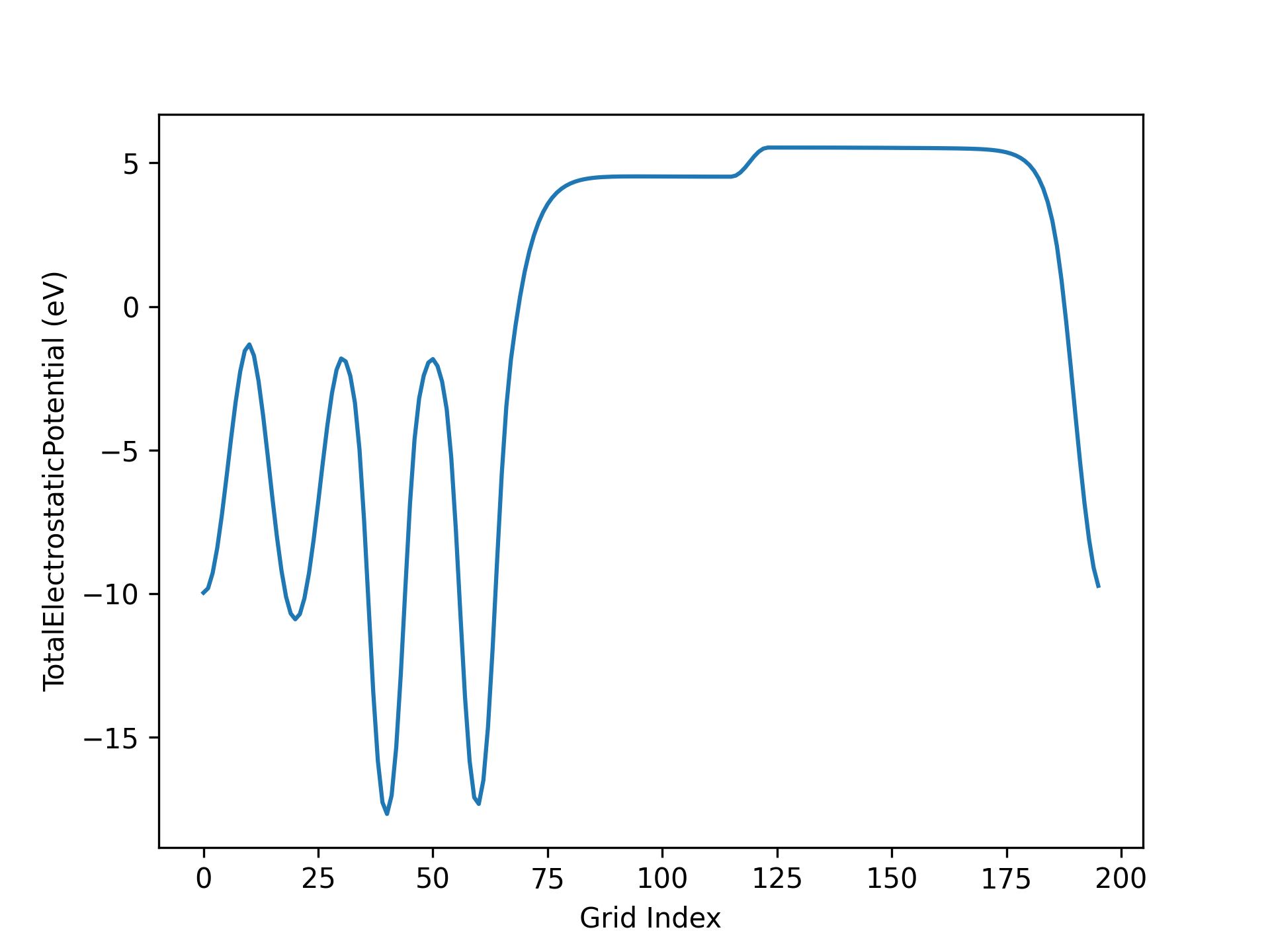
AuAl势函数示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
8.4 band能带数据处理
知识点:
脚本中调用get_band_data()读取数据,在读取数据时设置efermi=XX可将能量零点修改为指定值;设置zero_to_efermi=True, 可将能量零点修改问所读取的文件中的费米能级处
脚本调用pymatgen的BSPlotter.get_plot()画图,在画图时可设置zero_to_efermi=True,将坐标轴能量零点修改到费米能级处。由于pymatgen在2023.8.17的一处关键更新将绘图函数返回对象从plt改成了axes,导致后续脚本可能出现不兼容。因此用户脚本相关部分已添加一个判断语句加以处理。
能带两步算需从第一步自洽计算获取准确费米能级(从自洽获得的system.json),若获取失败,用户可在调用get_band_data读取数据时,利用参数efermi修改能量零点。例如:band_data=get_band_data('band.h5',efermi=-1.5)
脚本中画图调用pymatgen中的BSPlotter.get_plot, 当判断体系为非金属时,设置zero_to_efermi会认为VBM为费米能级能量而非文件读取时的费米能级。故当体系为非金属时,在数据读取时设置zero_to_efermi=True和在画图时设置zero_to_efermi=True得到的图会有区别
执行本节所列的python脚本,程序会判断是否为金属体系。若为非金属体系,将要求选择是否平移费米能级到能量零点,请按提示操作。
普通能带处理
参考 4bandplot.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
4from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import BSPlotter
5
6from dspawpy.io.read import get_band_data
7
8datafile = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/supplement/pband.h5" # Specifies the data file path
9band_data = get_band_data(
10 band_dir=datafile,
11 syst_dir=None, # path to system.json file, required only when band_dir is a json file
12 efermi=None, # Used for manually correcting the Fermi level
13 zero_to_efermi=True, # For non-metallic systems, the zero point energy should be shifted to the Fermi level
14)
15
16bsp = BSPlotter(band_data)
17axes_or_plt = bsp.get_plot(
18 zero_to_efermi=False, # The data has already been shifted when read, so this should be turned off
19 ylim=[-10, 10], # Range of the y-axis for the band structure plot
20 smooth=False, # Whether to smooth the band structure plot
21 vbm_cbm_marker=False, # Whether to mark the valence band maximum and conduction band minimum in the band structure plot
22 smooth_tol=0, # Threshold for smoothing
23 smooth_k=3, # Order of the smoothing process
24 smooth_np=100, # Number of points for smoothing
25)
26
27if isinstance(axes_or_plt, plt.Axes):
28 fig = axes_or_plt.get_figure() # version newer than v2023.8.10
29else:
30 fig = axes_or_plt.gcf() # older version pymatgen
31
32# Add a reference line for the energy zero point
33for ax in fig.axes:
34 ax.axhline(0, lw=2, ls="-.", color="gray")
35
36figname = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/4bandplot.png" # Filename for the output band plot
37os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(figname)), exist_ok=True)
38fig.savefig(figname, dpi=300)
知识点:
能带两步算需从自洽计算获取准确的费米能级(从system.json获取),若获取失败,用户可在 get_band_data 函数中指定 efermi 参数修改
执行代码可以得到类似以下能带图:
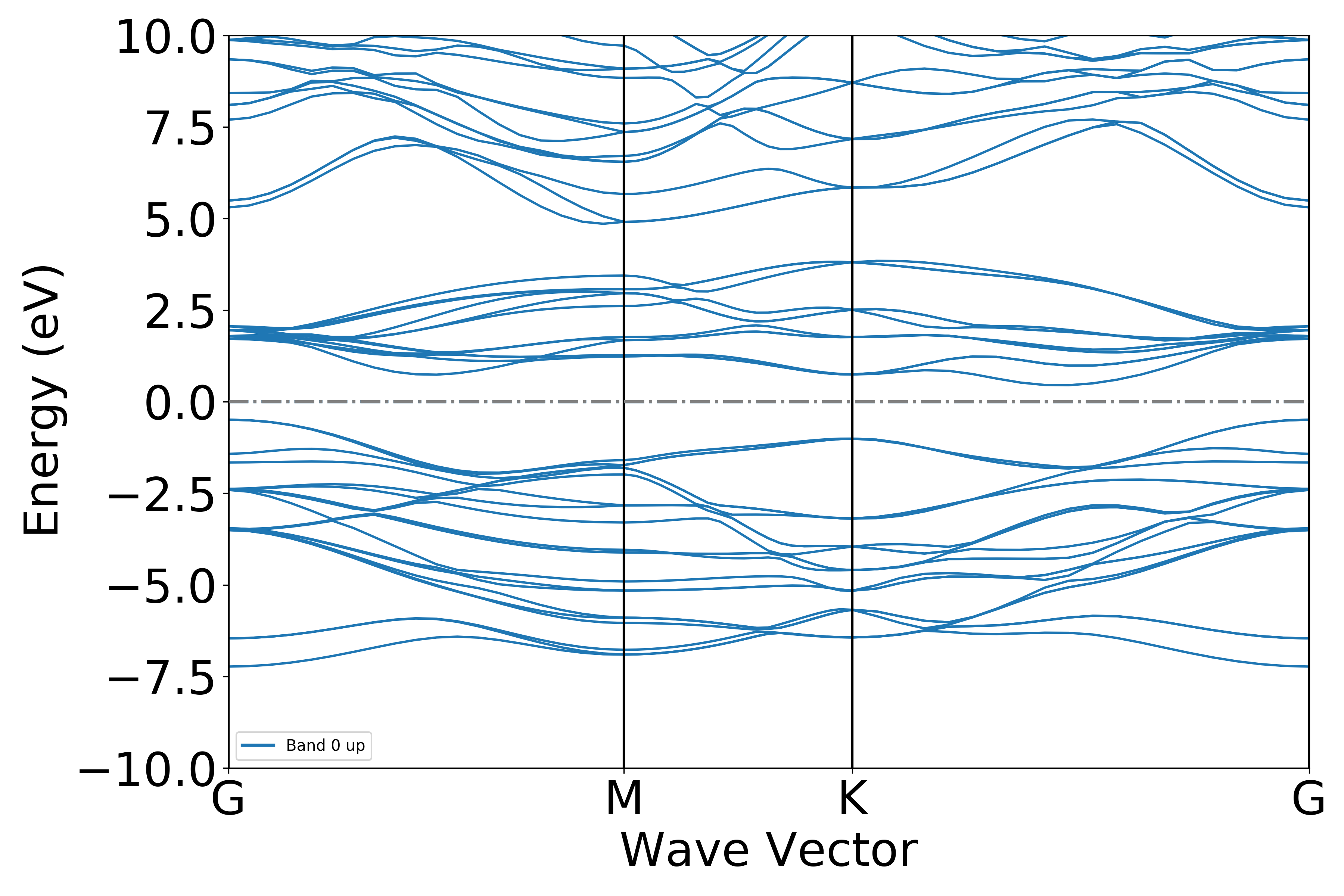
二硫化钼能带示意图
将能带投影到每一种元素分别作图,数据点大小表示该元素对该轨道的贡献
参考 4bandplot_elt.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
5import numpy as np
6from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import BSPlotterProjected
7
8from dspawpy.io.read import get_band_data
9
10datafile = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/supplement/pband.h5" # Specify the data file path
11band_data = get_band_data(
12 band_dir=datafile,
13 syst_dir=None, # path to system.json file, required only when band_dir is a json file
14 efermi=None, # Used to manually adjust the Fermi level
15 zero_to_efermi=True, # For non-metallic systems, shift the zero-point energy to the Fermi level
16)
17
18bsp = BSPlotterProjected(bs=band_data) # Initialize the BSPlotterProjected class
19axes_or_plt = bsp.get_elt_projected_plots(
20 zero_to_efermi=False, # The data has already been shifted when read, so this should be disabled
21 ylim=[-8, 5], # Set the energy range
22 vbm_cbm_marker=False, # Whether to mark the conduction band minimum (CBM) and valence band maximum (VBM)
23)
24
25if isinstance(axes_or_plt, plt.Axes):
26 fig = axes_or_plt.get_figure() # version newer than v2023.8.10
27elif np.iterable(axes_or_plt):
28 fig = np.asarray(axes_or_plt).flatten()[0].get_figure()
29else:
30 fig = axes_or_plt.gcf() # older version pymatgen
31
32# Add a reference line for the energy zero point
33for ax in fig.axes:
34 ax.axhline(0, lw=2, ls="-.", color="gray")
35
36figname = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/4bandplot_elt.png" # The filename for the output band plot
37os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(figname)), exist_ok=True)
38fig.savefig(figname, dpi=300)
知识点:
用户如果需要绘制能带投影的数据,此时需要使用 BSPlotterProjected模块
使用 BSPlotterProjected模块中 get_elt_projected_plots 函数能够绘制每种元素对轨道贡献的能带图
执行代码可以得到类似以下能带图:
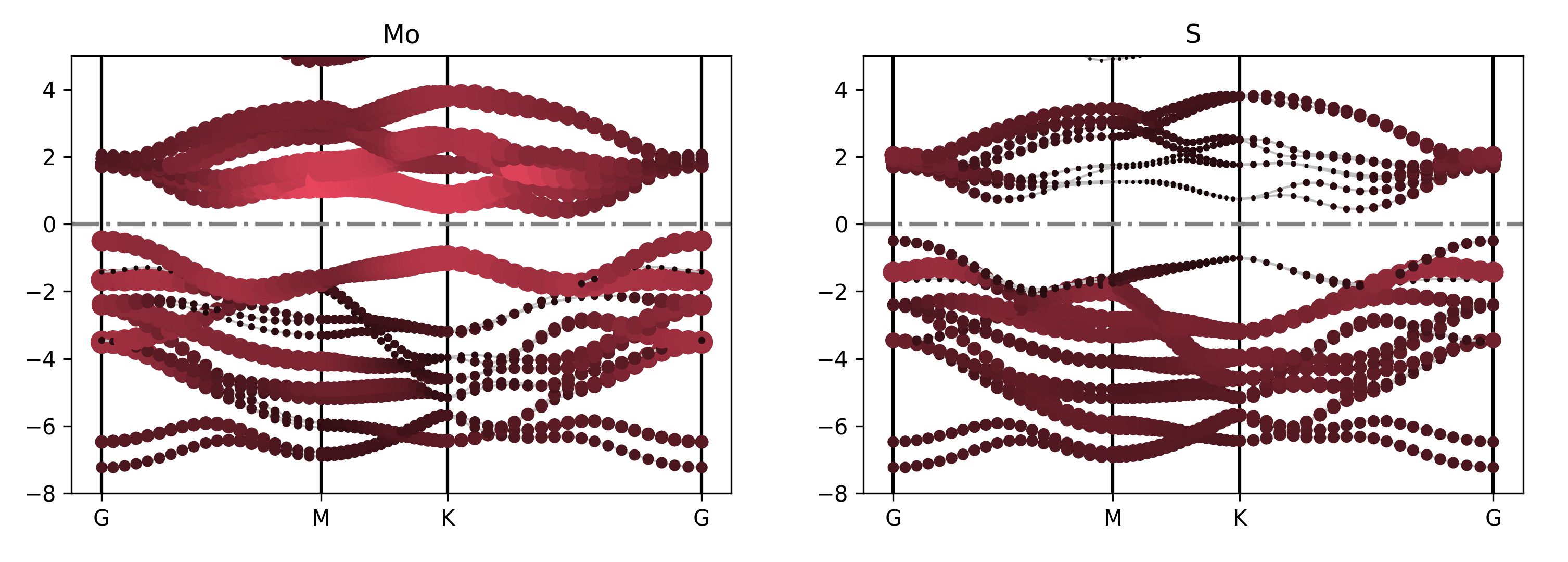
二硫化钼元素投影能带示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
能带投影到不同元素的不同轨道
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
5import numpy as np
6from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import BSPlotterProjected
7
8from dspawpy.io.read import get_band_data
9
10datafile = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/supplement/pband.h5" # Specify the data file path
11band_data = get_band_data(
12 band_dir=datafile,
13 syst_dir=None, # path to system.json file, only required when band_dir is a json file
14 efermi=None, # Used for manually correcting the Fermi level
15 zero_to_efermi=True, # For non-metallic systems, shift the zero point energy to the Fermi level
16)
17
18bsp = BSPlotterProjected(bs=band_data) # Initialize the BSPlotterProjected class
19# Select elements and orbitals, create a dictionary
20dict_elem_orbit = {"Mo": ["d"], "S": ["s"]}
21
22axes_or_plt = bsp.get_projected_plots_dots(
23 dictio=dict_elem_orbit,
24 zero_to_efermi=False, # The data has already been shifted when read, so this should be turned off
25 ylim=[-8, 5], # Set the energy range
26 vbm_cbm_marker=False, # Whether to mark the conduction band minimum and valence band maximum
27)
28
29if isinstance(axes_or_plt, plt.Axes):
30 fig = axes_or_plt.get_figure() # version newer than v2023.8.10
31elif np.iterable(axes_or_plt):
32 fig = np.asarray(axes_or_plt).flatten()[0].get_figure()
33else:
34 fig = axes_or_plt.gcf() # older version pymatgen
35
36# Add a reference line for the energy zero point
37for ax in fig.axes:
38 ax.axhline(0, lw=2, ls="-.", color="gray")
39
40figname = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/4bandplot_elt_orbit.png" # Filename for the output band plot
41os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(figname)), exist_ok=True)
42fig.savefig(figname, dpi=300)
知识点:
使用 BSPlotterProjected模块中 get_projected_plots_dots可以让用户来自定义需要绘制的某种元素某种轨道(L)的能带图
例如 get_projected_plots_dots ({'Mo':['d'],'S':['s']})就是绘制Mo的d轨道和S的s轨道
执行代码可以得到类似以下能带图:
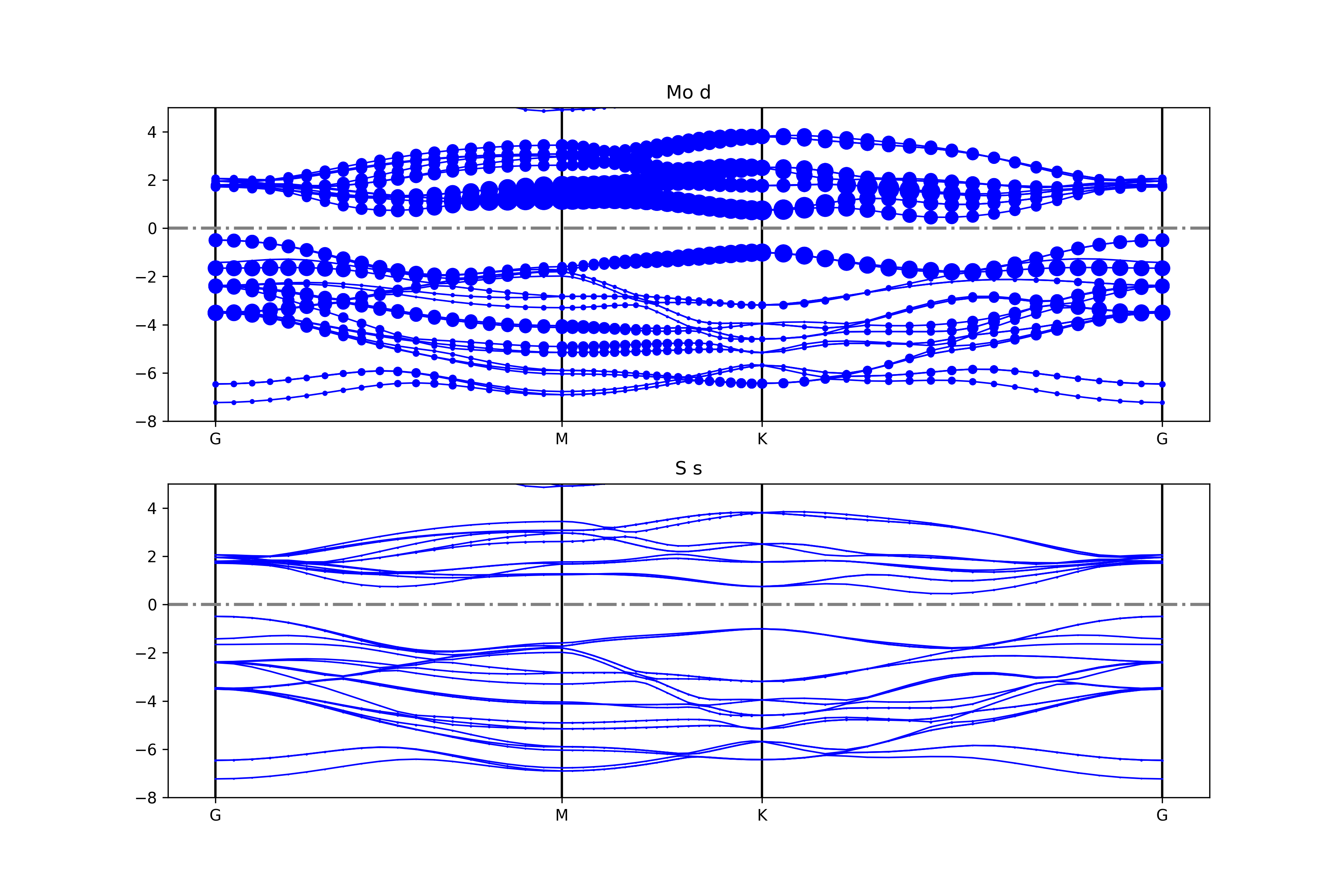
二硫化钼元素轨道投影能带示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
将能带投影到不同原子的不同轨道
参考 4bandplot_patom_porbit.py :
1# coding:utf-8 2import os 3 4import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5import numpy as np 6from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import BSPlotterProjected 7 8from dspawpy.io.read import get_band_data 9 10datafile = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/supplement/pband.h5" # Specify the data file path 11band_data = get_band_data( 12 band_dir=datafile, 13 syst_dir=None, # path to system.json file, required only when band_dir is a JSON file 14 efermi=None, # Used to manually adjust the Fermi level 15 zero_to_efermi=True, # For non-metallic systems, shift the zero point energy to the Fermi level 16) 17 18bsp = BSPlotterProjected(bs=band_data) 19# Specify elements, orbitals, and atomic numbers 20dict_elem_orbit = {"Mo": ["px", "py", "pz"]} 21dict_elem_index = {"Mo": [1]} 22 23axes_or_plt = bsp.get_projected_plots_dots_patom_pmorb( 24 dictio=dict_elem_orbit, # Specify the element-orbit dictionary 25 dictpa=dict_elem_index, # Specify the element-atomic number dictionary 26 sum_atoms=None, # Whether to sum over atoms 27 sum_morbs=None, # Whether to sum orbitals 28 zero_to_efermi=False, # Data has already been shifted during reading, should be turned off here 29 ylim=None, # Set the energy range 30 vbm_cbm_marker=False, # Whether to mark the conduction band minimum and valence band maximum 31 selected_branches=None, # Specify the energy band branches to be plotted 32 w_h_size=(12, 8), # Set image width and height 33 num_column=None, # Number of images displayed per row 34) 35 36if isinstance(axes_or_plt, plt.Axes): 37 fig = axes_or_plt.get_figure() # version newer than v2023.8.10 38elif np.iterable(axes_or_plt): 39 fig = np.asarray(axes_or_plt).flatten()[0].get_figure() 40else: 41 fig = axes_or_plt.gcf() # older version pymatgen 42 43# Add a reference line for the energy zero point 44for ax in fig.axes: 45 ax.axhline(0, lw=2, ls="-.", color="gray") 46 47figname = " dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/4band_patom_porbit.png" # Output bandpass figure filename 48os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(figname)), exist_ok=True) 49fig.savefig(figname, dpi=300)
知识点:
使用 BSPlotterProjected模块中 get_projected_plots_dots_patom_pmorb 的自由度更高,可以让用户来自定义需要绘制的某些原子某些轨道的能带图
dictpa指定原子,dictio 指定该原子的轨道
如果要将一些原子或一些轨道的投影分量叠加起来,请根据 get_projected_plots_dots_patom_pmorb 函数文档指定 sum_atoms 或 sum_morbs 参数
警告
如果只选择单个轨道,且轨道名称不止一个字母(例如px、dxy、dxz),get_projected_plots_dots_patom_pmorb 函数将报错,详情见 此处
执行代码可以得到类似以下能带图:
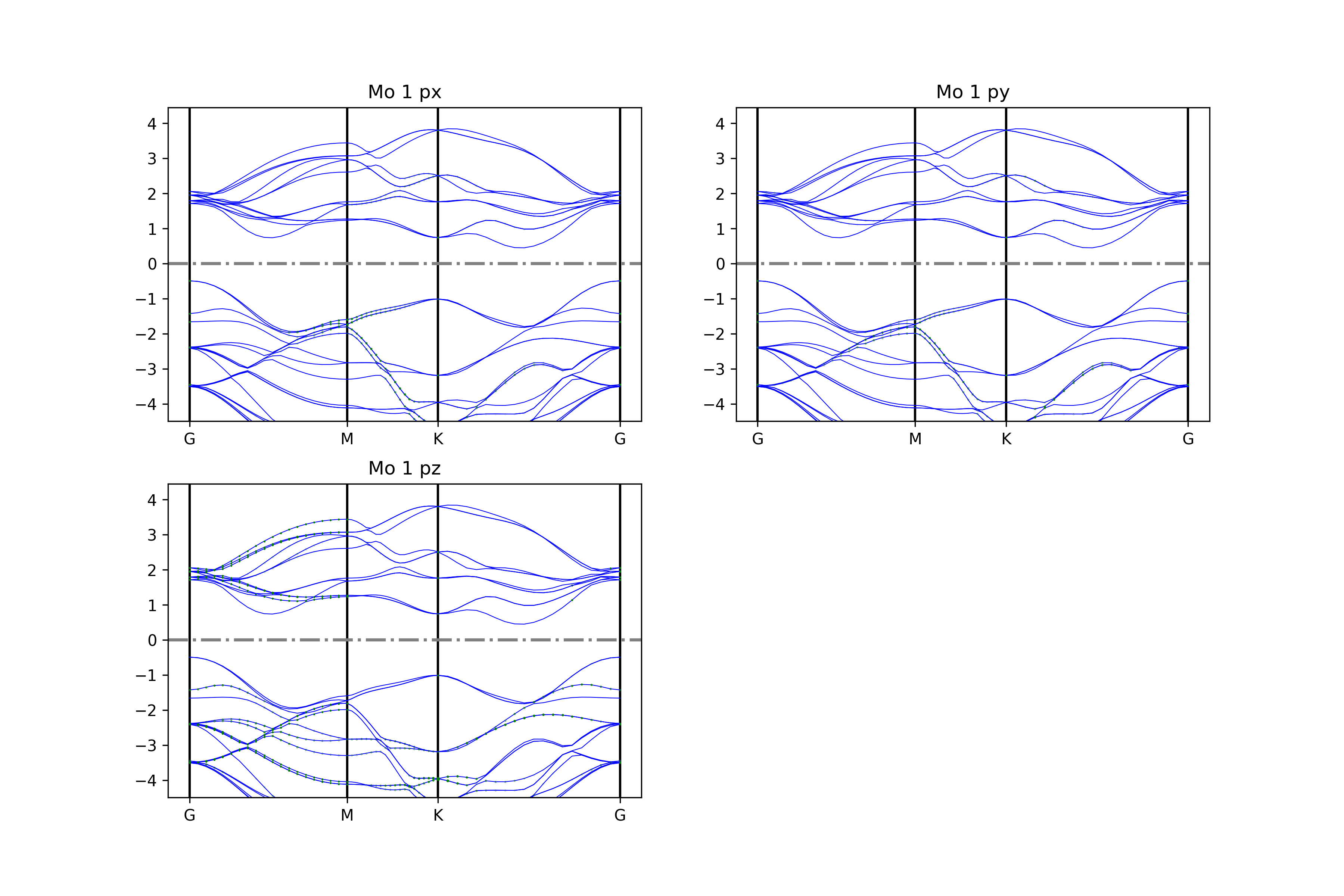
二硫化钼原子投影能带示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
能带反折叠处理
参考 4bandunfolding.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4from dspawpy.plot import plot_bandunfolding
5
6plt = plot_bandunfolding(
7 datafile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.22.1/band.h5", # Read data
8 ef=None, # Fermi level, read from the file
9 de=0.05, # Band width, default 0.05
10 dele=0.06, # Band gap, default 0.06
11)
12
13plt.ylim(-15, 10)
14figname = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/4bandunfolding.png" # Output band structure plot filename
15os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(figname)), exist_ok=True)
16plt.savefig(figname, dpi=300)
17# plt.show()
执行代码可以得到类似以下能带图:
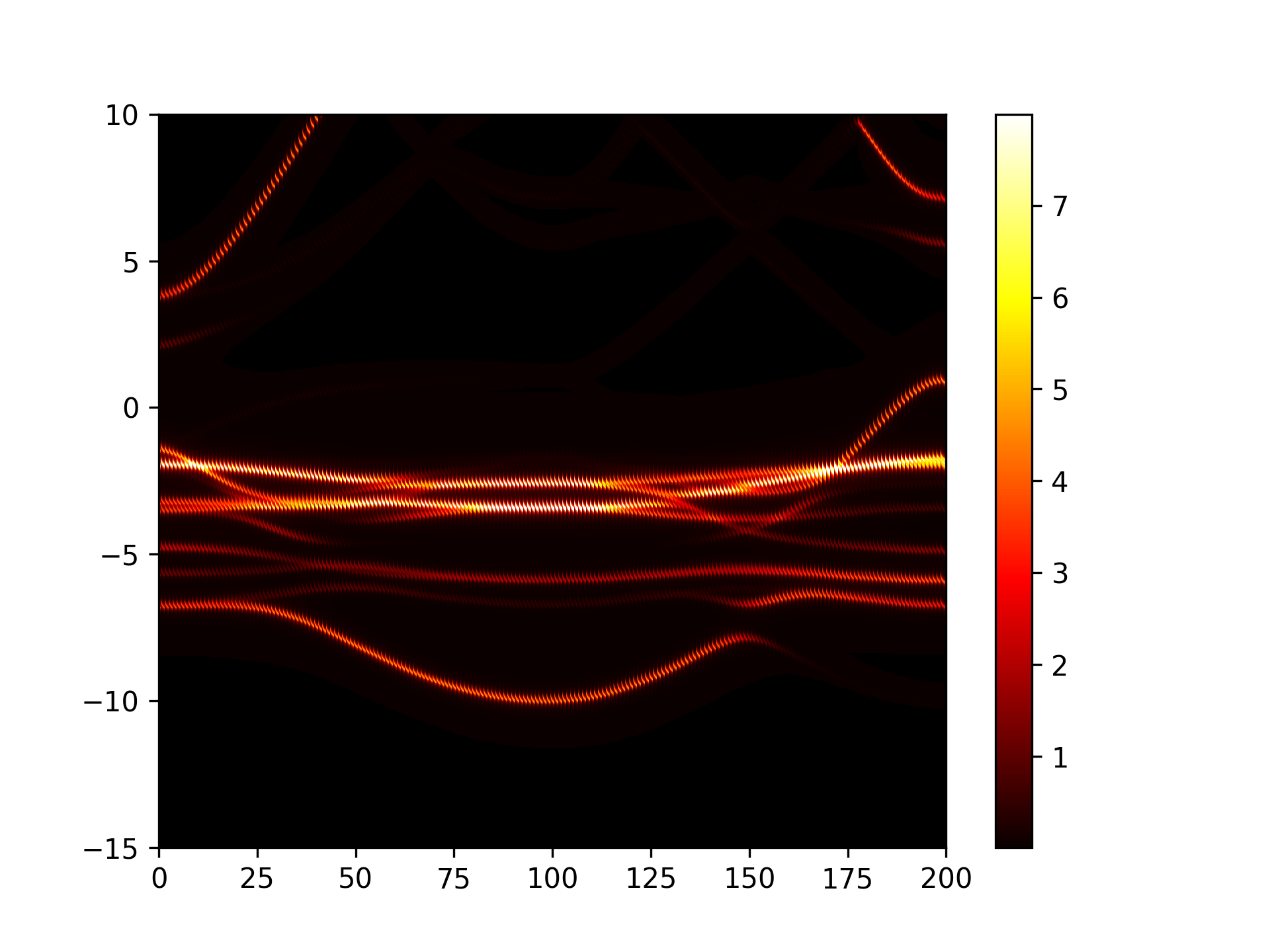
Cu3Au能带反折叠示意图
警告
此功能暂不支持将非金属材料的费米能级设为能量零点(默认价带顶为能量零点)。
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
band-compare能带对比图处理
将普通能带和wannier能带绘制在同一张图上
参考 4bandcompare.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import BSPlotter
5
6from dspawpy.io.read import get_band_data
7
8band_data = get_band_data(
9 band_dir="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.30/wannier.h5", # Wannier band file path
10 syst_dir=None, # system.json file path, only needed when band_dir is a json file
11 efermi=None, # Used for manually adjusting the Fermi level
12 zero_to_efermi=False, # Whether to shift zero energy to the Fermi level
13)
14bsp = BSPlotter(bs=band_data)
15band_data = get_band_data(
16 band_dir="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.3/band.h5", # Read DFT band structure
17 syst_dir=None, # path to system.json file, required only when band_dir is a json file
18 efermi=None, # Used for manually correcting the Fermi level
19 zero_to_efermi=False, # Whether to shift the zero point energy to the Fermi level
20)
21
22bsp2 = BSPlotter(bs=band_data)
23bsp.add_bs(bsp2._bs)
24axes_or_plt = bsp.get_plot(
25 zero_to_efermi=True, # Move the zero energy level to the Fermi level
26 ylim=[-10, 10], # Energy band plot y-axis range
27 smooth=False, # Whether to smooth the band structure plot
28 vbm_cbm_marker=False, # Whether to mark the valence band maximum and conduction band minimum in the band structure plot
29 smooth_tol=0, # Threshold for smoothing
30 smooth_k=3, # Order of the smoothing process
31 smooth_np=100, # Number of points for smoothing
32 bs_labels=["wannier interpolated", "DFT"], # Band structure labels
33)
34
35import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # noqa: E402
36
37if isinstance(axes_or_plt, plt.Axes):
38 fig = axes_or_plt.get_figure() # version newer than v2023.8.10
39else:
40 fig = axes_or_plt.gcf() # older version pymatgen
41
42# Add a reference line for the energy zero point
43for ax in fig.axes:
44 ax.axhline(0, lw=2, ls="-.", color="gray")
45
46figname = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/4wanierBand.png" # File name for the output band structure plot
47os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(figname)), exist_ok=True)
48fig.savefig(figname, dpi=300)
执行代码可得到类似如下能带对比曲线:
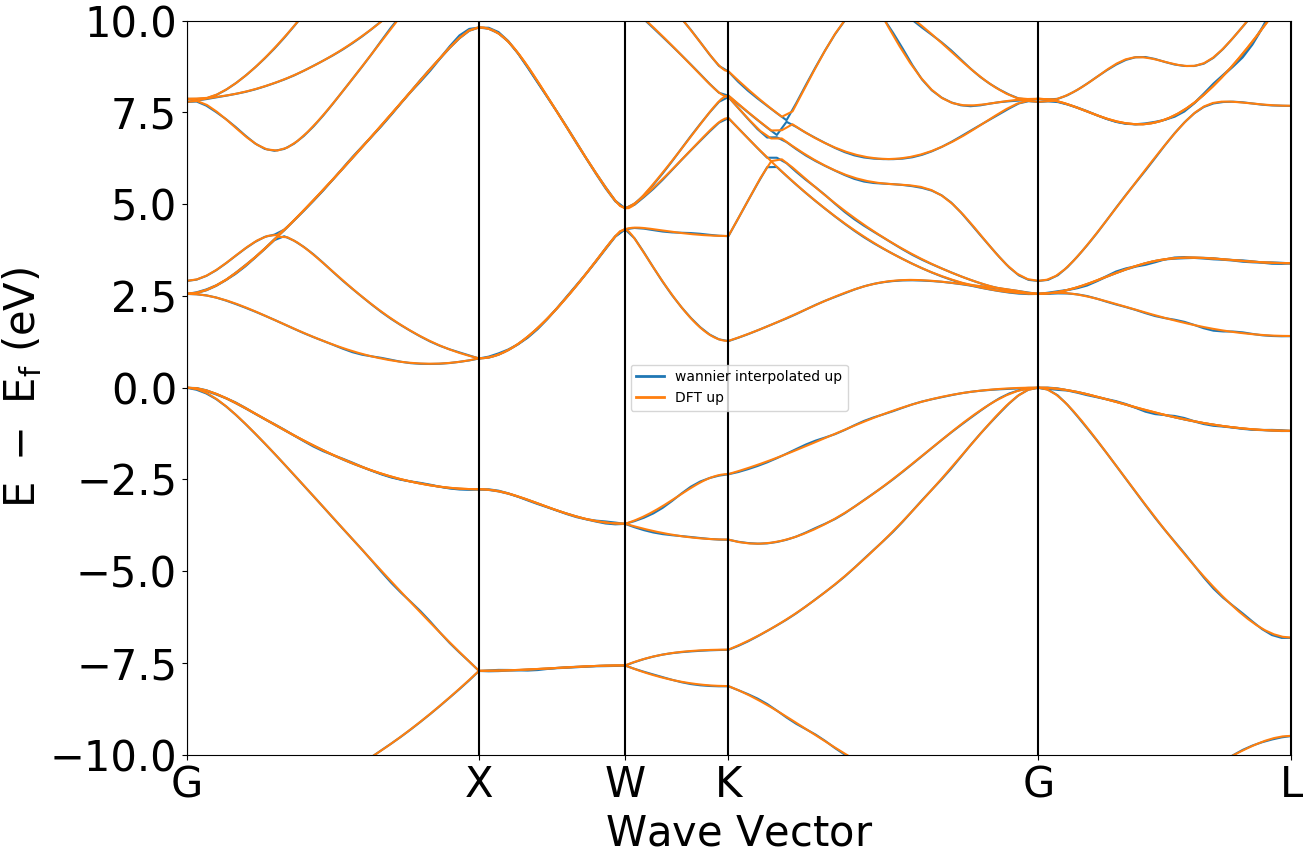
晶体硅瓦尼尔能带与DFT能带示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
8.5 dos态密度数据处理
总的态密度
参考 5dosplot_total.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import DosPlotter
5
6from dspawpy.io.read import get_dos_data
7from dspawpy.plot import plot_dos
8
9dos_data = get_dos_data(
10 dos_dir="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/3.2.4/dos.h5", # Read projected density of states data
11 return_dos=False, # If False, always return a CompleteDos object (regardless of whether projection was enabled during calculation)
12)
13dos_plotter = DosPlotter(
14 zero_at_efermi=True, # Whether to set the Fermi level as the zero point
15 stack=False, # True indicates drawing an area chart
16 sigma=None, # Gaussian broadening, None indicates no smoothing process
17)
18dos_plotter.add_dos(
19 label="total dos", dos=dos_data
20) # Set the legend for the density of states plot # Pass the density of states data
21
22ax = plot_dos(
23 dosplotter=dos_plotter,
24 xlim=[-10, 5], # Set the energy range
25 ylim=[-15, 15], # Set the density of states range
26)
27ax.axhline(0, lw=2, ls="-.", color="gray")
28
29filename = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/5dos_total.png" # File name for the output density of states plot
30os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(filename)), exist_ok=True)
31
32fig = ax.get_figure()
33fig.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
知识点:
使用 get_dos_data 函数可以将DS-PAW计算得到的 dos.h5 文件转化为 pymatgen 支持的格式
使用 DosPlotter模块获取到DS-PAW计算的 dos.h5 的数据
DosPlotter函数可以传递参数:stack参数表示画态密度是否加阴影, zero_at_efermi 表示是否在态密度图中进行将费米能量置零,这里设置 stack=False , zero_at_efermi=False
使用 DosPlotter 模块中 add_dos 获取态密度的数据
DosPlotter模块中 get_plot函数 绘制态密度图
执行代码可以得到类似以下态密度图:
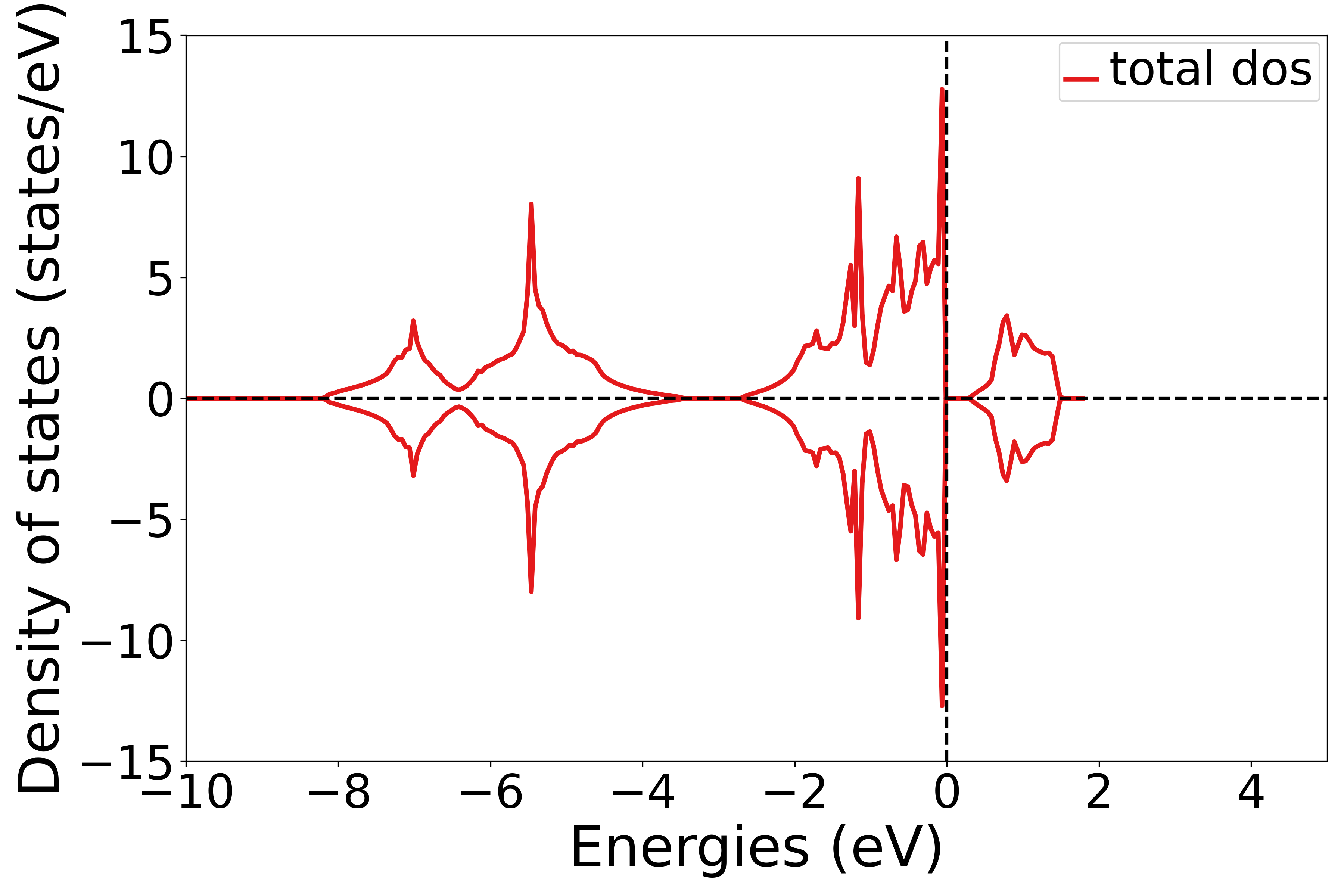
NiO态密度示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
将态密度投影到不同的轨道上
参考 5dosplot_spd.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import DosPlotter
5
6from dspawpy.io.read import get_dos_data
7from dspawpy.plot import plot_dos
8
9dos_data = get_dos_data(
10 dos_dir="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/3.2.4/dos.h5", # Read projected DOS data
11 return_dos=False, # If False, always return a CompleteDos object (regardless of whether projection was enabled during calculation)
12)
13dos_plotter = DosPlotter(
14 zero_at_efermi=True, # Whether to set the Fermi level as the zero point
15 stack=False, # True indicates drawing an area chart
16 sigma=None, # Gaussian broadening, None indicates no smoothing is applied
17)
18dos_plotter.add_dos_dict(
19 dos_dict=dos_data.get_spd_dos(),
20 key_sort_func=None, # Orbital projection # Specifies the sorting function
21)
22ax = plot_dos(
23 dosplotter=dos_plotter,
24 xlim=[-10, 5], # Set the energy range
25 ylim=None, # Set the density of states range
26)
27
28ax.axhline(0, lw=2, ls="-.", color="gray")
29
30filename = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/5dos_spd.png" # Filename of the output density of states plot
31os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(filename)), exist_ok=True)
32
33fig = ax.get_figure()
34fig.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
知识点:
使用 DosPlotter模块中 add_dos_dict 函数 获取投影态密度的数据,之后使用 get_spd_dos 将投影信息按照 spd 轨道投影输出
执行代码可以得到类似以下态密度图:
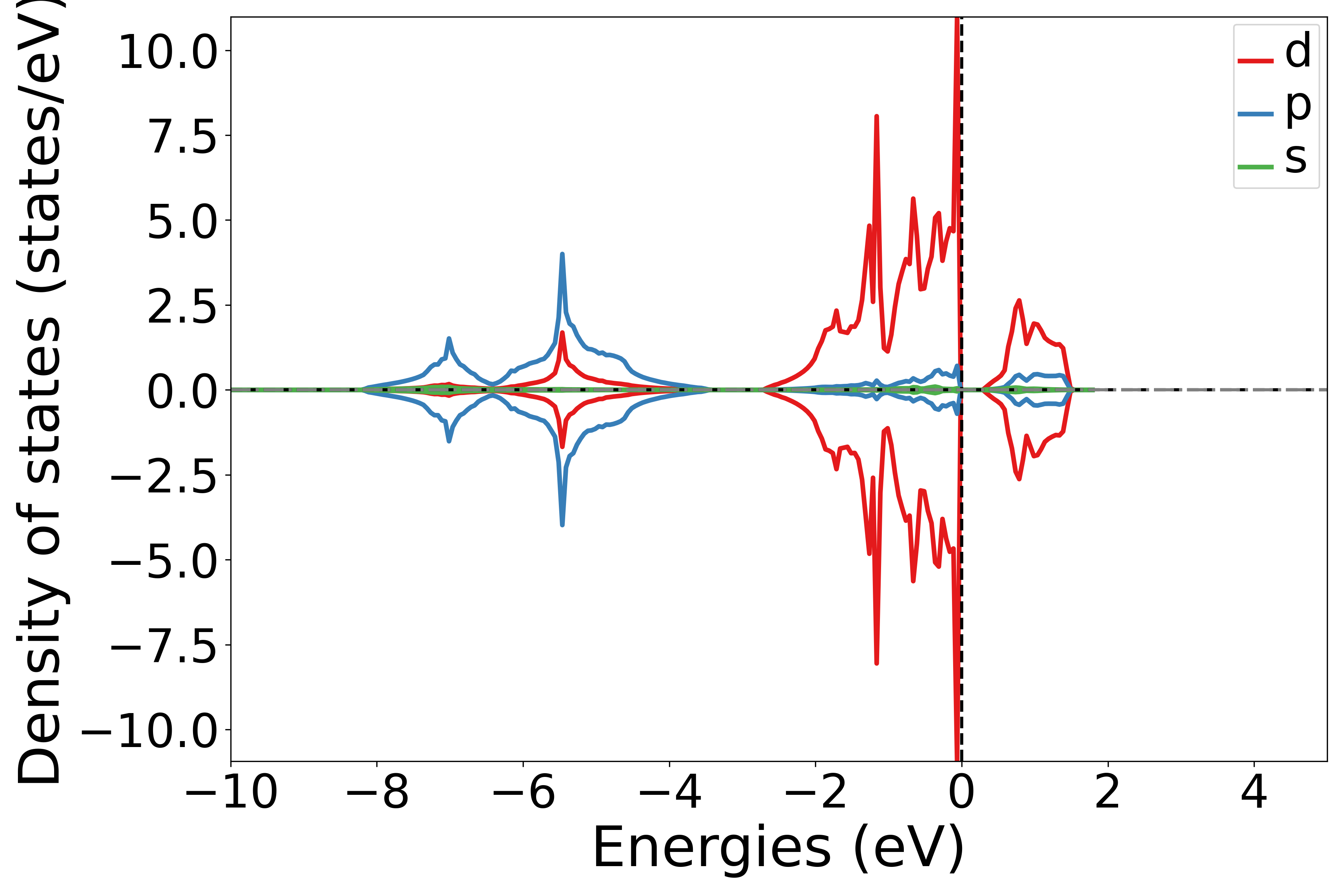
NiO轨道投影态密度示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
将态密度投影到不同的元素上
参考 5dosplot_elt.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import DosPlotter
5
6from dspawpy.io.read import get_dos_data
7from dspawpy.plot import plot_dos
8
9dos_data = get_dos_data(
10 dos_dir="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/3.2.4/dos.h5", # Reads projected DOS data
11 return_dos=False, # If False, always returns a CompleteDos object (regardless of whether projection was enabled during calculation)
12)
13dos_plotter = DosPlotter(
14 zero_at_efermi=True, # Whether to set the Fermi level as the zero point
15 stack=False, # True indicates drawing an area chart
16 sigma=None, # Gaussian broadening, None indicates no smoothing is applied
17)
18dos_plotter.add_dos_dict(
19 dos_dict=dos_data.get_element_dos(),
20 key_sort_func=None, # Projected DOS for elements # Specify the sorting function
21)
22
23ax = plot_dos(
24 dosplotter=dos_plotter,
25 xlim=[-10, 5], # Set the energy range
26 ylim=None, # Set the density of states range
27)
28ax.axhline(0, lw=2, ls="-.", color="gray")
29
30filename = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/5dos_elt.png" # Filename for the output density of states plot
31os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(filename)), exist_ok=True)
32
33fig = ax.get_figure()
34fig.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
知识点:
使用 DosPlotter模块中 add_dos_dict 函数 获取投影态密度的数据,之后使用 get_element_dos 将投影信息按照不同元素投影输出
执行代码可以得到类似以下态密度图:
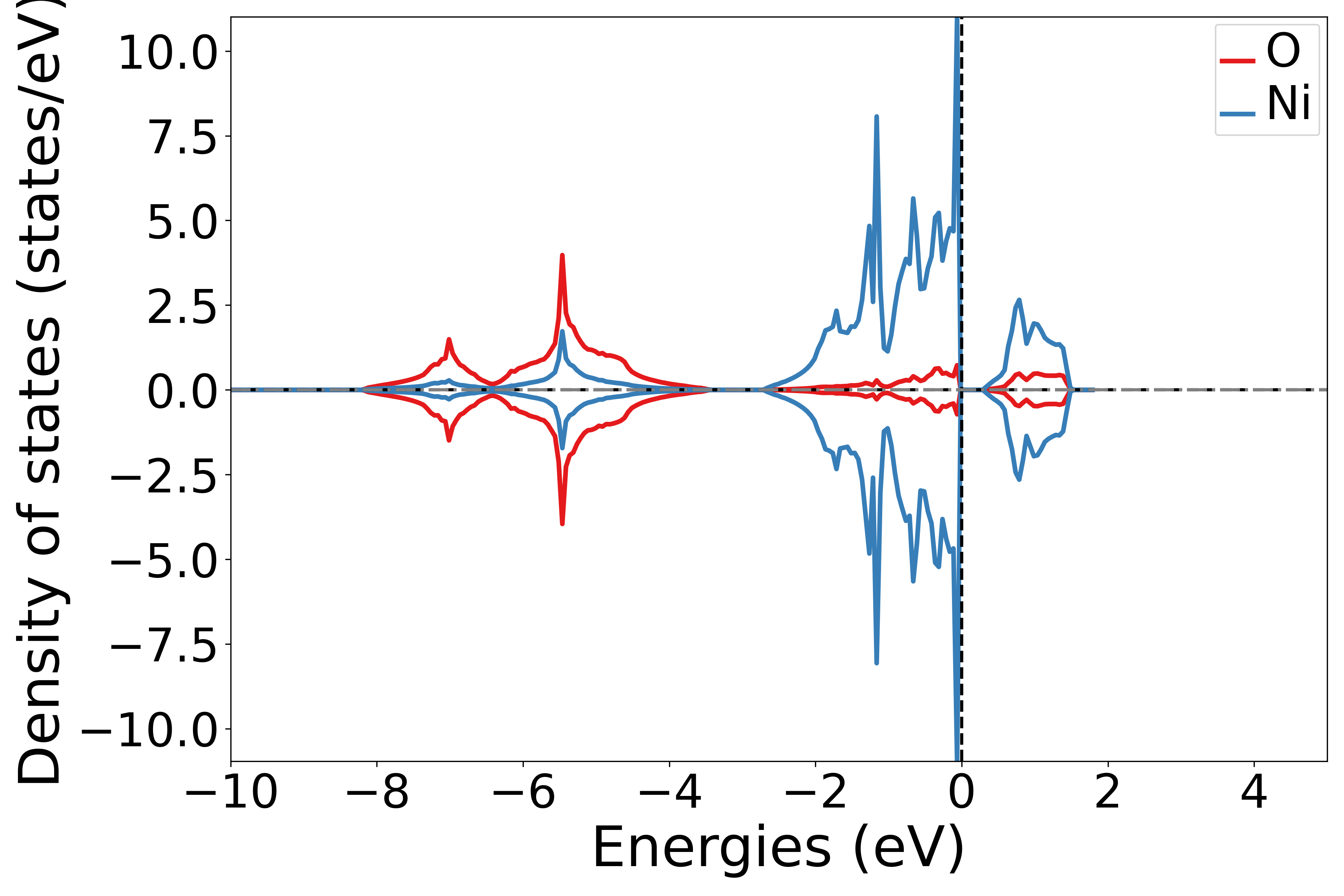
NiO元素投影态密度示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
将态密度投影到不同原子的不同轨道上
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4from pymatgen.electronic_structure.core import Orbital
5from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import DosPlotter
6
7from dspawpy.io.read import get_dos_data
8from dspawpy.plot import plot_dos
9
10dos_data = get_dos_data(
11 dos_dir="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/3.2.4/dos.h5", # Reads projected density of states data
12 return_dos=False, # If False, always return a CompleteDos object (regardless of whether projection was enabled during calculation)
13)
14dos_plotter = DosPlotter(
15 zero_at_efermi=True, # Whether to set the Fermi level as the zero point
16 stack=False, # True indicates drawing an area plot
17 sigma=None, # Gaussian broadening, None indicates no smoothing treatment
18)
19
20# ! Specify atomic number and orbital
21dict_index_orbit = {0: ["dxy"], 2: ["s"]}
22
23print("Plotting...")
24for index in dict_index_orbit:
25 _os = dict_index_orbit[index]
26 _e = str(dos_data.structure.sites[index].species)
27 for _orb in _os:
28 dos_plotter.add_dos(
29 f"{_e}(atom-{index}) {_orb}", # label
30 dos_data.get_site_orbital_dos(
31 dos_data.structure[index],
32 getattr(Orbital, _orb),
33 ),
34 )
35
36ax = plot_dos(
37 dosplotter=dos_plotter,
38 xlim=[-10, 5], # Set the energy range
39 ylim=None, # Set the density of states range
40)
41ax.axhline(0, lw=2, ls="-.", color="gray")
42
43figname = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/5dos_atom_orbit.png" # Output density of states figure filename
44os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(figname)), exist_ok=True)
45
46fig = ax.get_figure()
47fig.savefig(figname, dpi=300)
知识点:
使用 get_site_orbital_dos函数提取dos数据中特定原子特定轨道的贡献,dos_data.structure[0],Orbital(4) 表示获取第1个原子的dxy轨道的态密度,get_site_orbital_dos函数中序号从0开始
运行此脚本,根据提示选择元素和轨道,可以得到相应的态密度图
执行代码可以得到类似以下态密度图:
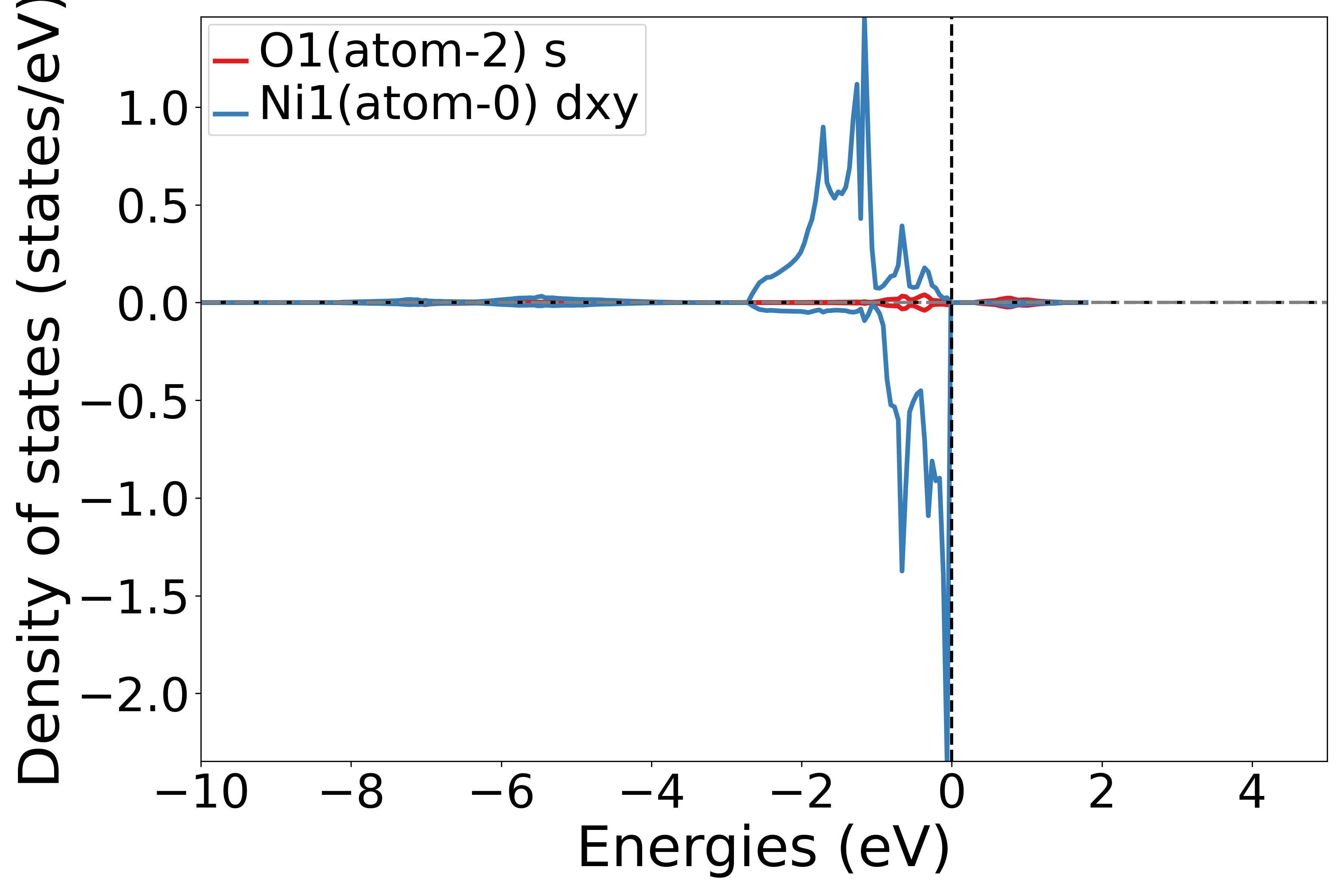
NiO原子轨道态密度示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
将态密度投影到不同原子的分裂d轨道(t2g, eg)上
参考 5dosplot_t2g_eg.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import DosPlotter
5
6from dspawpy.io.read import get_dos_data
7from dspawpy.plot import plot_dos
8
9dos_data = get_dos_data(
10 dos_dir="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/3.2.4/dos.h5", # Read projected density of states data
11 return_dos=False, # If False, always returns a CompleteDos object (regardless of whether projection was enabled during calculation)
12)
13dos_plotter = DosPlotter(
14 zero_at_efermi=True, # Whether to set the Fermi level as the zero point
15 stack=False, # True indicates drawing an area chart
16 sigma=None, # Gaussian broadening, None indicates no smoothing is applied
17)
18# print(dos_data.structure)
19
20# Specify the atomic number, starting from 0
21ais = [1]
22
23print("Plotting...")
24atom_indices = [int(ai) for ai in ais]
25for atom_index in atom_indices:
26 dos_plotter.add_dos_dict(
27 dos_data.get_site_t2g_eg_resolved_dos(dos_data.structure[atom_index]),
28 )
29
30ax = plot_dos(
31 dosplotter=dos_plotter,
32 xlim=[-10, 5], # Set the energy range
33 ylim=None, # Set the density of states range
34)
35ax.axhline(0, lw=2, ls="-.", color="gray")
36
37filename = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/5dos_t2g_eg.png" # Output density of states plot filename
38os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(filename)), exist_ok=True)
39
40fig = ax.get_figure()
41fig.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
知识点:
使用 get_site_t2g_eg_resolved_dos函数 提取dos数据中特定原子的 t2g和 eg轨道的贡献,这是获取第2个原子的t2g和eg轨道的贡献
运行此脚本,根据提示选择原子序号,可以得到相应的态密度图
执行代码可以得到类似以下态密度图:
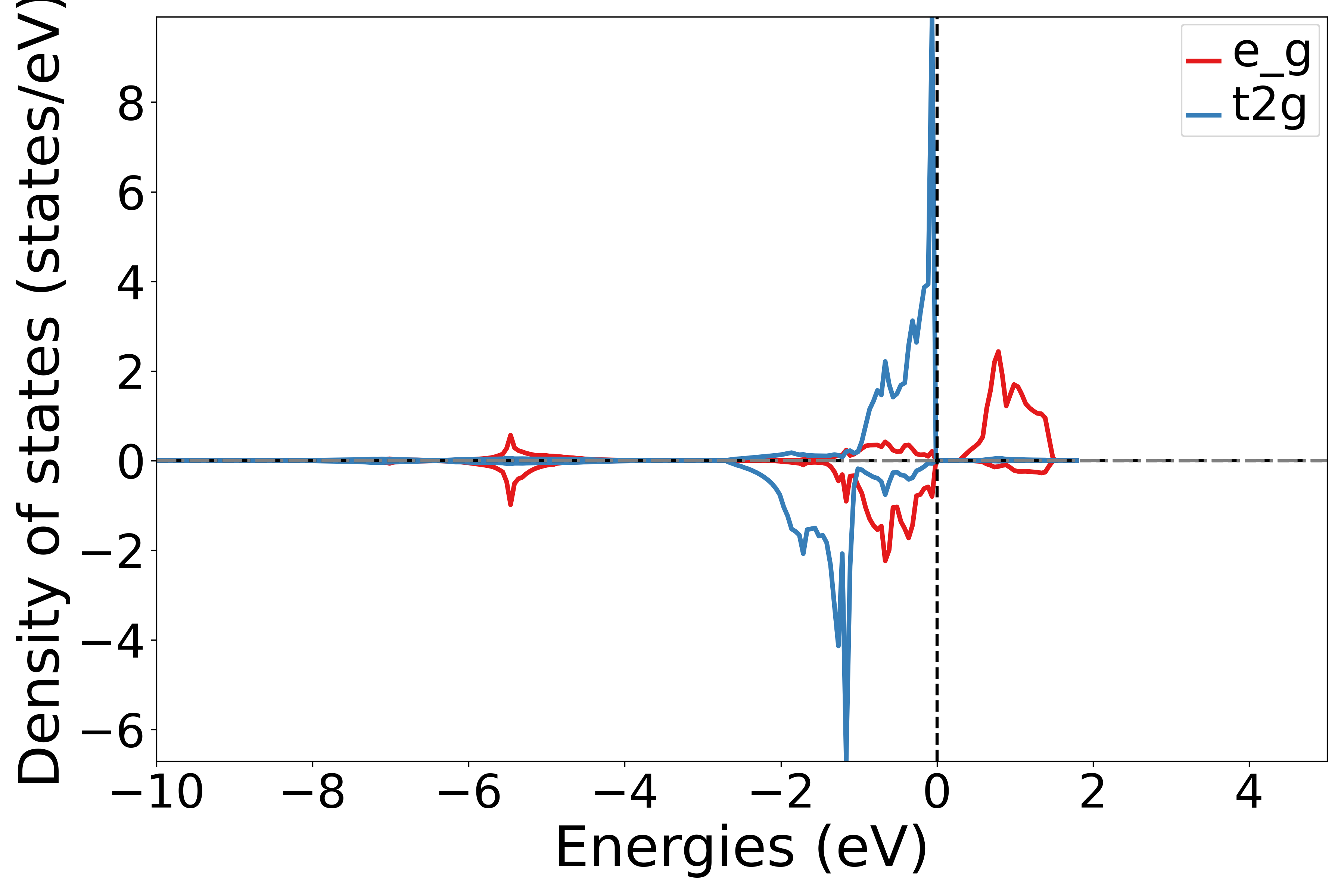
NiO分裂d轨道原子投影态密度示意图
知识点:
如果元素不含d轨道,会画成空白图片
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
d-带中心分析
以 Pb-slab 体系为例,对 Pt 原子进行 d-band 中心分析:
参考 5center_dband.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2from dspawpy.io.read import get_dos_data
3from dspawpy.io.utils import d_band
4
5dos_data = get_dos_data(
6 dos_dir="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/supplement/dos.h5", # Read projected density of states data
7 return_dos=False, # If False, always returns a CompleteDos object (regardless of whether projection was enabled during calculation)
8)
9for spin in dos_data.densities:
10 print("spin=", spin)
11 c = d_band(spin, dos_data)
12 print(c)
执行代码可以得到类似以下结果:
spin=1
-1.785319344084034
备注
目前仅支持全部原子平均的 d 轨道中心,不支持元素、原子投影或其他轨道,也不支持选择自旋方向或能量范围。
get_dos_data 函数负责处理态密度数据:
8.6 bandDos能带和态密度共同显示
以应用教程中Si体系为例:
将能带和态密度显示在一张图上
参考 6bandDosplot.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4import numpy as np
5from matplotlib.axes import Axes
6from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import BSDOSPlotter
7
8from dspawpy.io.read import get_band_data, get_dos_data
9
10bandfile = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.3/band.h5" # Normal band data
11band_data = get_band_data(
12 band_dir=bandfile,
13 syst_dir=None, # path to system.json file, required only when band_dir is a json file
14 efermi=None, # Used for manually correcting the Fermi level
15)
16band_efermi = band_data.efermi
17dosfile = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.5/dos.h5" # Density of states data
18dos_data = get_dos_data(
19 dos_dir=dosfile,
20 return_dos=False, # If False, always return a CompleteDos object (regardless of whether projection was enabled during calculation)
21)
22dos_efermi = dos_data.efermi
23bdp = BSDOSPlotter(
24 bs_projection=None, # Band structure projection method, None means no projection
25 dos_projection=None, # Projection method for density of states, None means no projection
26 vb_energy_range=4, # Valence band energy range
27 cb_energy_range=4, # Conduction band energy range
28 fixed_cb_energy=False, # Whether to fix the conduction band energy range
29 egrid_interval=1, # Energy grid interval
30 font="DejaVu Sans", # Default is Times New Roman, change to DejaVu Sans to avoid warnings due to missing font on Linux
31 axis_fontsize=20, # Axis font size
32 tick_fontsize=15, # Tick label font size
33 legend_fontsize=14, # Legend font size
34 bs_legend="best", # Band structure legend position
35 dos_legend="best", # Density of States legend position
36 rgb_legend=True, # Use colored legend
37 fig_size=(11, 8.5), # Figure size
38)
39if band_efermi != dos_efermi:
40 print(f"{band_efermi=:.4f} eV")
41 print(f"{dos_efermi=:.4f} eV")
42 d_efermi = band_efermi - dos_efermi
43
44 print(
45 "! Band and DOS Fermi levels are inconsistent, using DOS Fermi level as reference"
46 )
47 band_data.bands = {spin: v + d_efermi for spin, v in band_data.bands.items()}
48
49 # ! Band and DOS Fermi levels are inconsistent, using Band level as the reference
50 # dos_data.energies -= d_efermi
51
52axes_or_plt = bdp.get_plot(
53 bs=band_data, dos=dos_data
54) # Pass band data # Pass density of states data
55
56if isinstance(axes_or_plt, Axes):
57 fig = axes_or_plt.get_figure() # version newer than v2023.8.10
58elif np.iterable(axes_or_plt):
59 fig = np.asarray(axes_or_plt).flatten()[0].get_figure()
60else:
61 fig = axes_or_plt.gcf() # older version pymatgen
62
63filename = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/6bandDos.png" # Filename for the band structure - density of states plot output
64os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(filename)), exist_ok=True)
65fig.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
66print("==> Saved", filename)
执行代码可以得到类似以下能带态密度图:
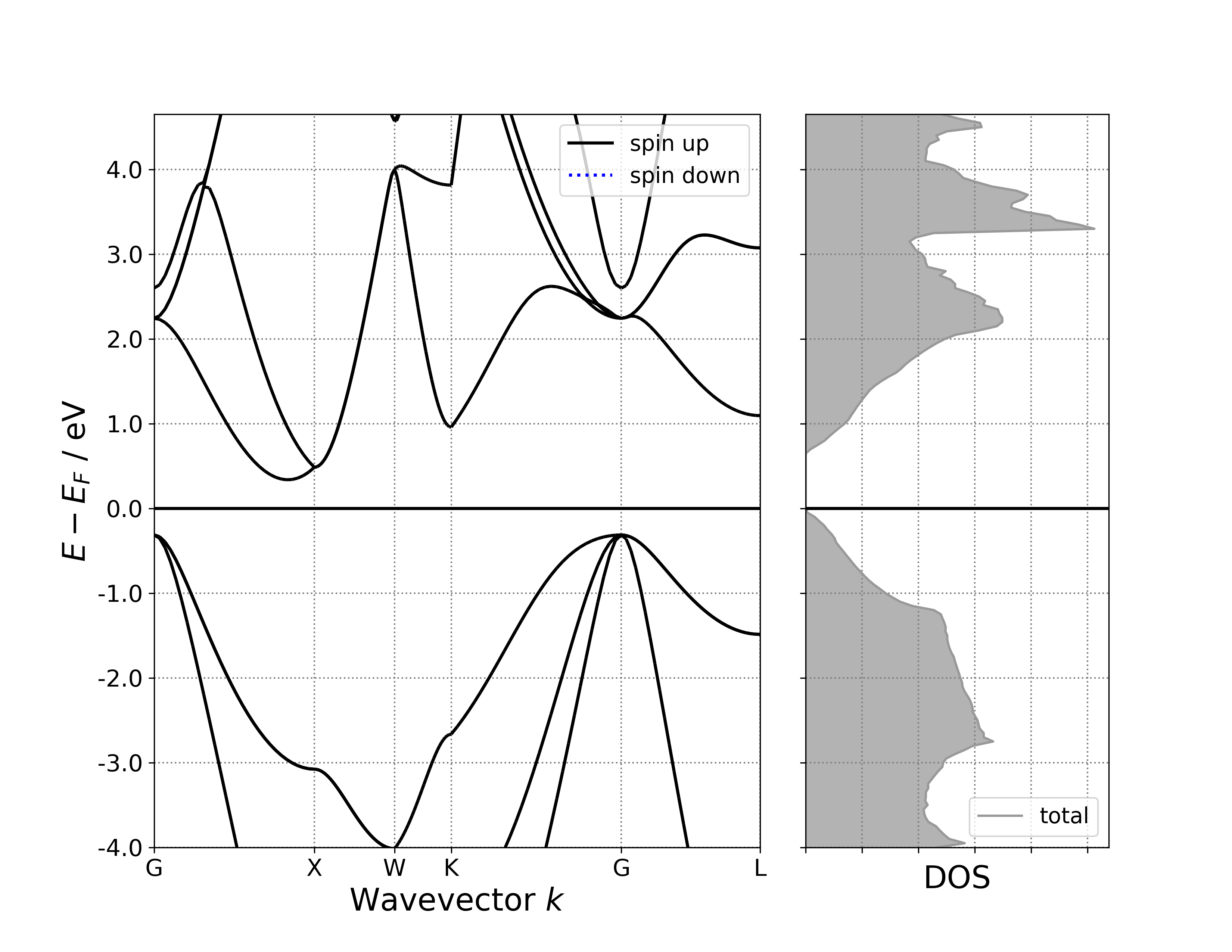
单晶硅能带-态密度示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
将能带和投影态密度显示在一张图上
参考 6bandPdosplot.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4import numpy as np
5from matplotlib.axes import Axes
6from pymatgen.electronic_structure.plotter import BSDOSPlotter
7
8from dspawpy.io.read import get_band_data, get_dos_data
9
10bandfile = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.4/band.h5" # Normal band data
11band_data = get_band_data(
12 band_dir=bandfile,
13 syst_dir=None, # path to system.json file, required only when band_dir is a json file
14 efermi=None, # Used for manually correcting the Fermi level
15)
16band_efermi = band_data.efermi
17dosfile = (
18 "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.6/dos.h5" # DOS data for projected states
19)
20dos_data = get_dos_data(
21 dos_dir=dosfile,
22 return_dos=False, # If False, always return a CompleteDos object (regardless of whether projection was enabled during calculation)
23)
24dos_efermi = dos_data.efermi
25bdp = BSDOSPlotter(
26 bs_projection="elements", # Projection method for band structure, None means no projection
27 dos_projection="elements", # Project DOS onto elements
28 vb_energy_range=4, # Valence band energy range
29 cb_energy_range=4, # Conduction band energy range
30 fixed_cb_energy=False, # Whether to fix the conduction band energy range
31 egrid_interval=1, # Energy grid interval
32 font="DejaVu Sans", # Default is Times New Roman, can be changed to DejaVu Sans to avoid warnings due to font not being installed on Linux
33 axis_fontsize=20, # Axis font size
34 tick_fontsize=15, # Tick label font size
35 legend_fontsize=14, # Legend font size
36 bs_legend="best", # Band structure legend position
37 dos_legend="best", # Position of the projected density of states legend
38 rgb_legend=True, # Use colored legend
39 fig_size=(11, 8.5), # Figure size
40)
41if band_efermi != dos_efermi:
42 print(f"{band_efermi=:.4f} eV")
43 print(f"{dos_efermi=:.4f} eV")
44 d_efermi = band_efermi - dos_efermi
45
46 print(
47 "! Band and DOS Fermi levels are inconsistent, using DOS Fermi level as reference"
48 )
49 band_data.bands = {spin: v + d_efermi for spin, v in band_data.bands.items()}
50
51 # ! Band and DOS Fermi levels are inconsistent, using Band level as reference
52 # dos_data.energies -= d_efermi
53
54axes_or_plt = bdp.get_plot(
55 bs=band_data,
56 dos=dos_data,
57) # Pass band structure data # Pass projected density of states data
58
59if isinstance(axes_or_plt, Axes):
60 fig = axes_or_plt.get_figure() # version newer than v2023.8.10
61elif np.iterable(axes_or_plt):
62 fig = np.asarray(axes_or_plt).flatten()[0].get_figure()
63else:
64 fig = axes_or_plt.gcf() # older version pymatgen
65
66filename = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/6bandPdos.png" # filename for the band structure-projected density of states plot
67os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(filename)), exist_ok=True)
68fig.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
69print("==> Saved", filename)
执行代码可以得到类似以下能带态密度图:

单晶硅能带-投影态密度示意图
警告
给定投影能带数据,默认将沿着元素投影;给定普通能带数据(或体系所含元素种类超过4种),则不投影,并输出警告
给定投影态密度数据,默认也将沿着元素投影,可以换成沿着轨道投影,或者不投影;给定普通态密度数据且未关闭态密度投影选项 BSDOSPlotter(dos_projection=None),pymatgen绘图程序将报错,这就是上面特意准备了一个 6bandDosplot.py 文件的原因。
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
8.7 optical光学性质数据处理
以快速入门Si体系光学性质计算得到的 scf.h5 为例(注:输出文件名与task一致,task = scf,io.optical = true可计算光学性质):
反射率数据处理,参考 7optical.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2from dspawpy.plot import plot_optical
3
4plot_optical(
5 datafile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.12/scf.h5",
6 keys=["ExtinctionCoefficient", "Reflectance"],
7 axes=["X"], # ["X", "Y", "Z", "XY", "YZ", "ZX"]
8 prefix="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/optical", # Where to save, if empty, it means the current folder
9 save=True, # Whether to save the image with the tool's name, if False, please refer to the script below to save manually
10)
11
12# The above function will plot and save the images of ExtinctionCoefficient and Reflectance separately
13# To plot multiple properties on the same figure, uncomment the following code and set the save parameter above to False
14
15# import os
16# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
17#
18# plt.tick_params(labelsize=16)
19# plt.tight_layout()
20# filename = "outputs/us/7optical.png" # Filename for the output optical properties plot
21# os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(filename)), exist_ok=True)
22# plt.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
知识点:
Reflectance为光学性质中的一种,用户可以根据自己的需求将该关键词修改为“AbsorptionCoefficient”或”ExtinctionCoefficient”或”RefractiveIndex”,分别对应吸收系数、消光系数和折射率
执行代码可以得到类似以下反射率随能量变化的曲线:
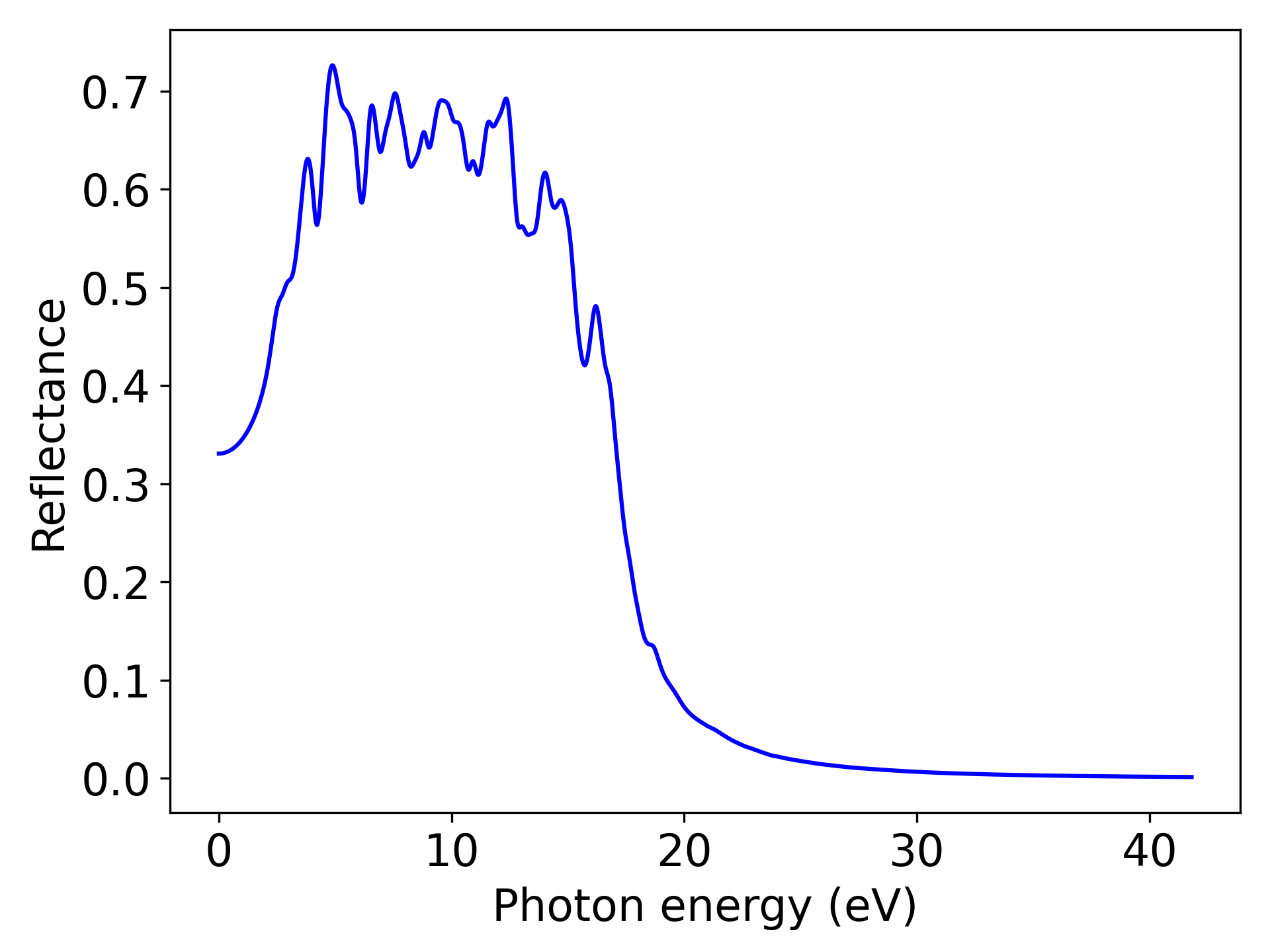
单晶硅Reflectance随光子能量变化趋势示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
8.8 neb过渡态计算数据处理
以快速入门 H 在 Pt(100) 表面扩散为例进行介绍:
输入文件之生成中间构型
参考
8neb_interpolate_structures.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.diffusion.neb import NEB, write_neb_structures 3from dspawpy.diffusion.nebtools import write_json_chain 4from dspawpy.io.structure import read 5 6# Read initial configuration 7init_struct = read("dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15/00/structure00.as")[0] 8# Read final state configuration 9final_struct = read("dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15/04/structure04.as")[0] 10 11neb = NEB( 12 initial_structure=init_struct, # Initial structure 13 final_structure=final_struct, # Final state configuration 14 nimages=8, # Total of 8 configurations, including initial and final states 15) 16structures = neb.linear_interpolate() # Linear interpolation 17# structures = neb.idpp_interpolate() # IDPP interpolation 18 19# Save as structure file to dest path 20write_neb_structures( 21 structures=structures, # Insert interpolated structure chains 22 coords_are_cartesian=True, # Whether to save in Cartesian coordinates 23 fmt="as", # Save format, supported formats: 'json', 'as', 'hzw', 'pdb', 'xyz', 'dump' 24 path="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb_interpolate_structures", # Save path 25 prefix="structure", # File name prefix 26) 27 28# Preview initial structure chain 29write_json_chain( 30 preview=True, # whether to enable preview mode 31 directory="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb_interpolate_structures", # Directory for NEB calculations 32 step=-1, # Default to saving the structure chain of the last ion step (latest) 33 dst="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb", # Save path 34) 35# write_xyz_chain(preview=True, # Whether to run in preview mode 36# directory="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb_interpolate_structures", # NEB calculation directory 37# step=-1, # Default to saving the structure chain of the last ionic step (latest) 38# dst='dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb' # save path 39# )
知识点:
用户可以根据需要自行修改插点个数,设置为8得到包含8个结构文件的文件夹,其中中间构型为6个
neb.linear_interpolate为线性插值方法,pbc参数为 True 时将锁定寻找最短扩散路径,默认为 False 以增加用户控制的灵活性,这是因为
举个例子,初态某原子的分数坐标是 0.2,终态变成 0.8。pbc = True 将强制设置扩散路径为 0.2 -> -0.2。pbc = False 则用户可以令程序按照 0.2 -> 0.8 的扩散路径进行插值;如果要用最短路径,手动将 0.8 改为 -0.2 即可,从而确保程序按照使用者的意图完成插值初猜。
绘制能垒图
neb.iniFin = true/false
当设置 neb.iniFin = true/false 时,都可使用读取neb计算的路径进行势垒分析(确保初末态计算文件在neb计算路径下):
参考
8neb_barrier_CubicSpline.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.diffusion.nebtools import plot_barrier 3 4directory_of_neb_task = ( 5 "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15" # <-- Please modify to the actual NEB path 6) 7 8# Plotting the energy barrier using CubicSpline interpolation 9plot_barrier( 10 directory=directory_of_neb_task, # path of the neb task 11 method="CubicSpline", # Cubic spline interpolation 12 figname="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb_barrier_CubicSpline.png", # Output filename for the energy barrier plot 13 show=False, # Whether to display the energy barrier plot 14)
备注
运行上述脚本后,可得到类似以下三次样条插值的势垒曲线:
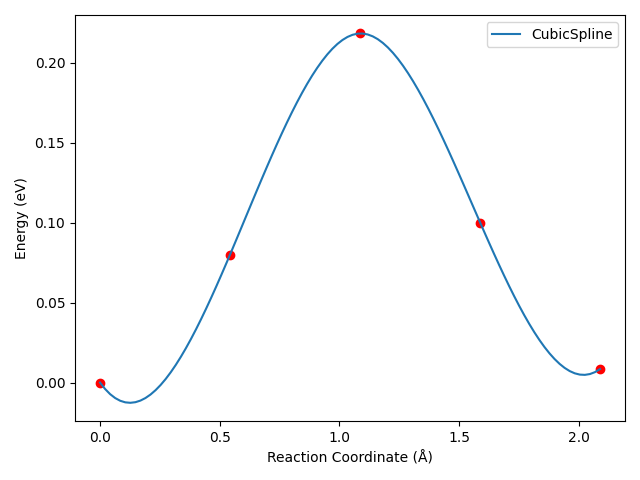
对于这个算例,三次样条插值后,曲线会出现不合理的“下坠”区域,这是三次样条插值算法的特性所决定的。
dspawpy 内部调用 scipy 的插值算法 ,上面这个脚本我们以三次样条插值算法为例,它在 scipy 文档中的定义为:
class scipy.interpolate.CubicSpline(x, y, axis=0, bc_type='not-a-knot', extrapolate=None)
关键词参数包括 axis, bc_type, extrapolate,具体含义见 scipy.interpolate.CubicSpline 。我们可以往 plot_barrier 函数中指定相应的关键词参数(axis, bc_type, extrapolate),将其传递给 scipy.interpolate.CubicSpline 这个类处理。
下面我们采用 8neb_barrier.py 脚本,对比三种算法插值绘制出的曲线:
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
5
6from dspawpy.diffusion.nebtools import plot_barrier
7
8# Compare the differences in energy barrier curves drawn by different interpolation methods, where show should be set to False
9# 1. interp1d
10plot_barrier(
11 directory="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15", # path for NEB calculation
12 ri=None, # Reaction coordinate between the initial structure and the second structure, required when the NEB task only calculated intermediate structures
13 rf=None, # Reaction coordinate between the last configuration and the second-to-last configuration, when the NEB task only calculated intermediate configurations
14 ei=None, # Energy of the initial configuration, required when the NEB task only calculated intermediate configurations
15 ef=None, # Energy of the final configuration, required when the NEB task only calculated intermediate configurations
16 method="interp1d", # Interpolation method
17 figname=None, # Name of the output energy barrier plot file
18 show=False, # Whether to display the energy barrier plot
19 kind="quadratic", # Parameter of the interpolation method
20)
21# 2. CubicSpline
22plot_barrier(
23 directory="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15",
24 method="CubicSpline",
25 figname=None,
26 show=False,
27)
28# 3. pchip
29plot_barrier(
30 directory="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15",
31 method="pchip",
32 figname=None,
33 show=False,
34)
35
36filename = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb_barrier_comparison.png" # Filename for the energy barrier plot output
37os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(filename)), exist_ok=True)
38plt.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
39# plt.show()
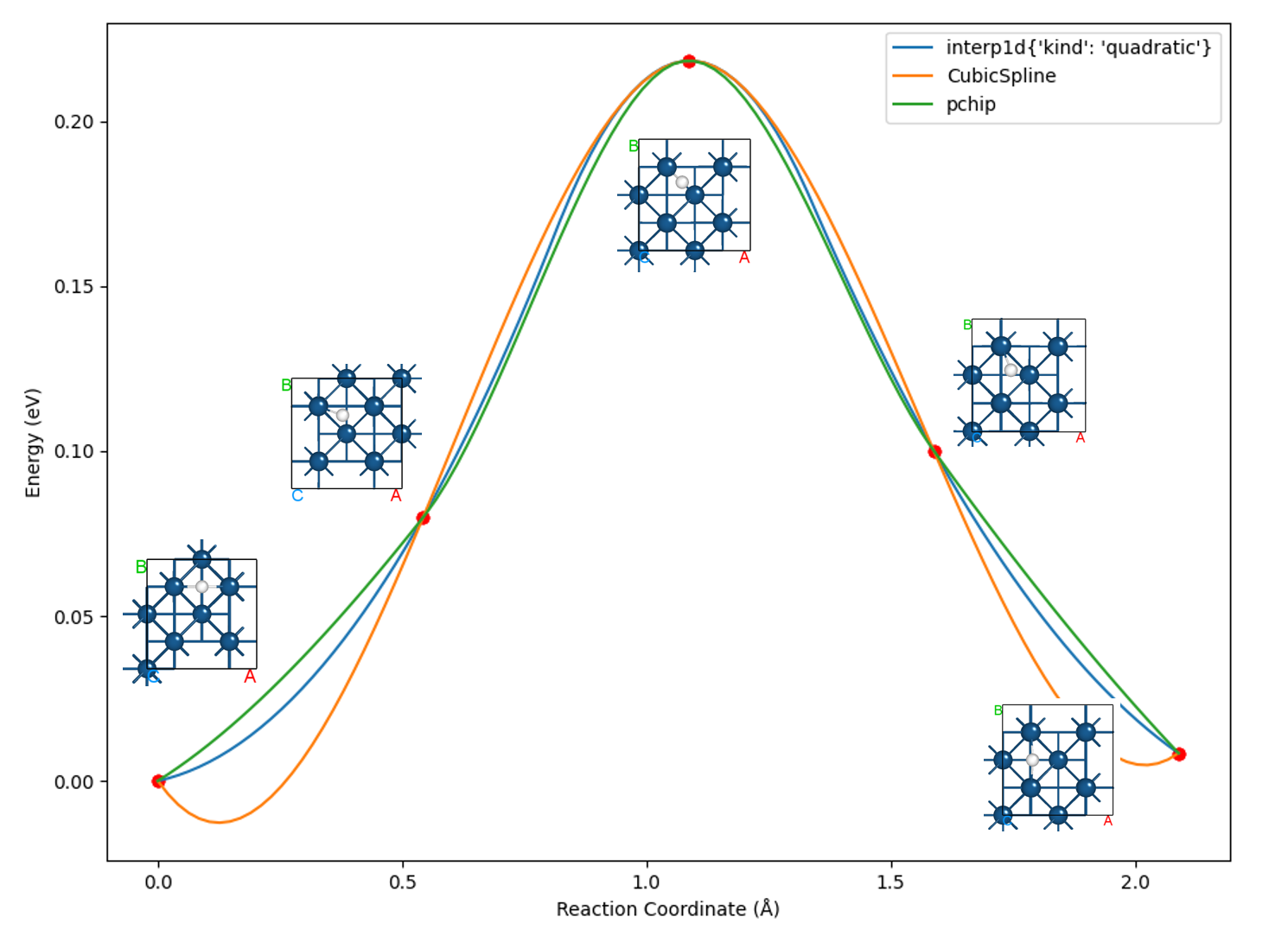
知识点:
选择合适的插值算法对于优化最终曲线的呈现效果至关重要
多数情况下,选择 pchip 这种单调三次样条插值算法即可达到较好效果,这也是默认调用的插值算法
neb.iniFin = true
当设置 neb.iniFin = true 时,读取neb计算所得的 neb.h5/neb.json 文件可快速进行势垒分析:
参考
8neb_barrier_CubicSpline.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.diffusion.nebtools import plot_barrier 3 4# Plot energy barrier using CubicSpline interpolation 5plot_barrier( 6 datafile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15/neb.h5", # Path to neb.h5 7 method="CubicSpline", # Cubic spline interpolation 8 figname="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb_barrier_.png", # Output file name for the energy barrier plot 9 show=False, # Whether to display the energy barrier plot 10)
处理得到的势垒图与之前读取路径效果一致。
备注
neb.h5 和 neb.json文件所存能量为TotalEnergy,如需得精确的势垒值,建议采用读取neb计算路径的方法进行处理(取TotalEnergy0)
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
过渡态计算数据处理
NEB计算完成后,一般要画出能垒图观察,并检查各插值构型最终的受力大小,从而确保受力小于指定的阈值。如果结果异常,还需要检查各插值构型在结构优化过程中的受力与能量变化趋势,判断是否真正“收敛”。上述这些操作至少需要三次循环,为简化操作,我们提供了一个一步到位的总结函数 summary :
-
1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.diffusion.nebtools import summary 3 4# Import the neb calculation directory, a complete folder after neb calculation needs to be provided 5summary( 6 directory="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15", 7 show_converge=False, # Whether to display the convergence plots of energy and force 8 outdir="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb", # Path to save convergence plots of energy and forces 9 figname="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb/neb_barrier_summary.png", # Path to save the energy barrier plot 10) 11# Additional keyword arguments can be set for plotting the barrier diagram, such as: 12# summary(directory='dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15', method='CubicSpline') # Change to CubicSpline for spline interpolation
知识点:
此脚本将以表格形式打印各构型的能量和受力、绘制能垒图,并绘制中间构型的能量与受力收敛过程图
若
neb.iniFin = false,用户必须将自洽计算的结果文件 scf.h5 或 system.json 文件复制到对应的初末态子文件夹中,否则程序无法读取初末态能量和受力信息,将报错退出默认情况下,能垒图存储在neb计算目录外层,各中间构型的能量与受力收敛图存储在各子文件夹
执行代码可以得到类似如下NEB计算各构型的能量和受力表格:
Image
Force (eV/Å)
Reaction coordinate (Å)
Energy (eV)
Delta energy (eV)
00
0.1803
0.0000
-39637.0984
0.0000
01
0.0263
0.5428
-39637.0186
0.0798
02
0.0248
1.0868
-39636.8801
0.2183
03
0.2344
1.5884
-39636.9984
0.1000
04
0.0141
2.0892
-39637.0900
0.0084
除了可以获得能垒图外,还可以得到各中间构型的能量和受力收敛曲线(以02构型为例)
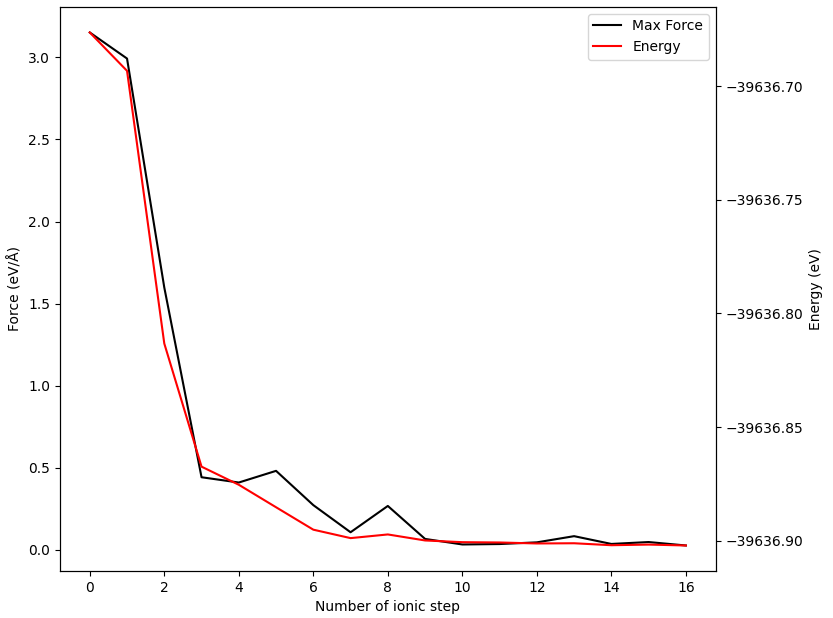
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
观察NEB链
此处所说NEB链指的是各插值构型(structure00.as, structure01.as, ...)之间的几何关系,而不是单个构型在优化过程中的变化。
NEB任务计算量较大,观察NEB链有助于判断NEB计算的收敛速度。另外,通过插值算法生成中间结构后,经常需要预览NEB链。这些需求可以通过
8neb_visualize.py脚本实现:
1# coding:utf-8
2from dspawpy.diffusion.nebtools import write_json_chain, write_xyz_chain
3
4# Convert the configuration chain under the NEB calculation path to a JSON format file
5write_json_chain(
6 preview=False, # If the NEB calculation is already completed, preview mode is not required
7 directory="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15", # NEB calculation directory
8 step=-1, # Default to saving the configuration chain of the last ion step (latest)
9 dst="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb", # Save path
10 ignorels=False, # Set to True to ignore latestStructureXX.as files
11)
12
13# Convert the configuration chain in the NEB calculation path to xyz format files
14write_xyz_chain(
15 preview=False, # If the NEB calculation is already completed, preview mode is not required
16 directory="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15", # NEB calculation directory
17 step=-1, # Default to saving the configuration chain of the last ionic step (latest)
18 dst="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb", # Save path
19 ignorels=False, # Set to True to ignore latestStructureXX.as files
20)
知识点:
此脚本生成neb_movie*.json文件后,通过
Device Studio-->Simulator-->DS-PAW-->Analysis Plot打开 json 文件即可观察directory指定为NEB计算主路径,需提供neb计算完成后的完整文件夹
该脚本支持处理正在进行中的(即未完成的)neb计算文件,方便用户监测实时轨迹
xyz文件可通过 OVITO 软件打开查看:通过
Device Studio-->Simulator-->OVITO打开可视化界面,将xyz文件拖入即可结构信息读取优先级:latestStructureXX.as > h5 > json;设置ignorels为True后,先尝试读取 h5 中的数据,失败则读取 json 中的数据
计算构型间距
参考这个脚本
8calc_dist.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.diffusion.nebtools import get_distance 3from dspawpy.io.structure import read 4 5# Please modify the paths of structure01.as and structure02.as structure files according to the actual situation 6# First read the fractional coordinates, element list, and cell information of the two configurations 7s1 = read("dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15/01/structure01.as")[0] 8s2 = read("dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15/02/structure02.as")[0] 9# Calculate the distance between the two configurations, note that this function only accepts fractional coordinates 10dist = get_distance( 11 spo1=s1.frac_coords, 12 spo2=s2.frac_coords, 13 lat1=s1.lattice.matrix, 14 lat2=s2.lattice.matrix, 15) 16print("The distance between the two configurations is:", dist, "Angstrom")
neb续算
如果需对neb进行续算,可参考
8neb_restart.py:1# coding:utf-8 2import os 3from shutil import copytree, rmtree 4 5from dspawpy.diffusion.nebtools import restart 6 7if os.path.isdir("dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/neb4bk"): 8 rmtree("dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/neb4bk") 9 10copytree( 11 "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.15", 12 "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/neb4bk", 13) 14restart( 15 directory="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/neb4bk", # NEB task path 16 output="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/8neb_restart", # Backup destination 17)
具体效果见 neb过渡态计算续算说明。
neb计算过程中能量和最大原子受力的变化趋势图
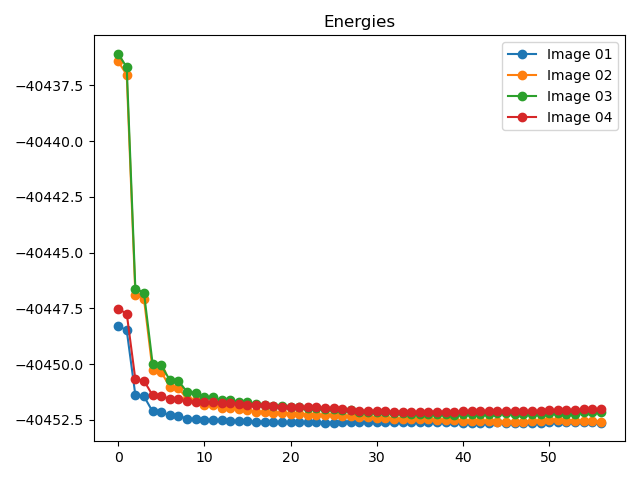
要查看neb计算过程中能量和最大原子受力的变化趋势图,可参考
8neb_energy_force_curves.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.diffusion.nebtools import monitor_force_energy 3 4# Specify the path to the NEB calculation folder; after running, Energies.png and MaxForce.png images will be generated in the specified directory 5unfinished_neb_folder = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/supplement/neb_unfinished" 6monitor_force_energy( 7 directory=unfinished_neb_folder, 8 outdir="imgs", # Output image path 9)
将生成能量和受力变化趋势图:
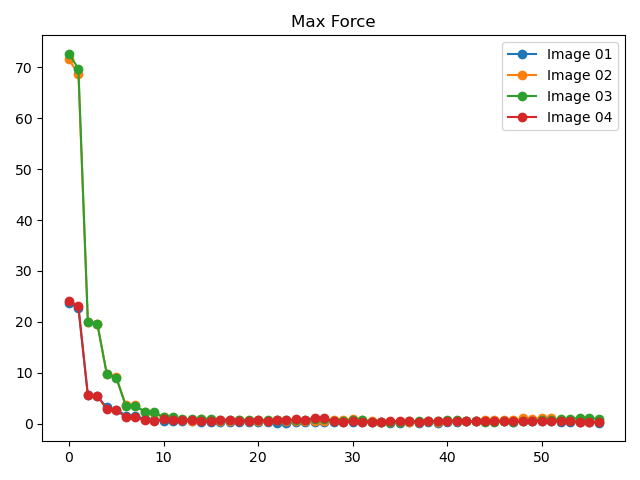
8.9 phonon声子计算数据处理
以MgO体系的声子能带态密度计算得到的 phonon.h5 为例:
如果未安装 phonopy,运行下列脚本时会弹出 no module named 'phonopy' 信息,不影响程序正常运行
声子能带数据处理
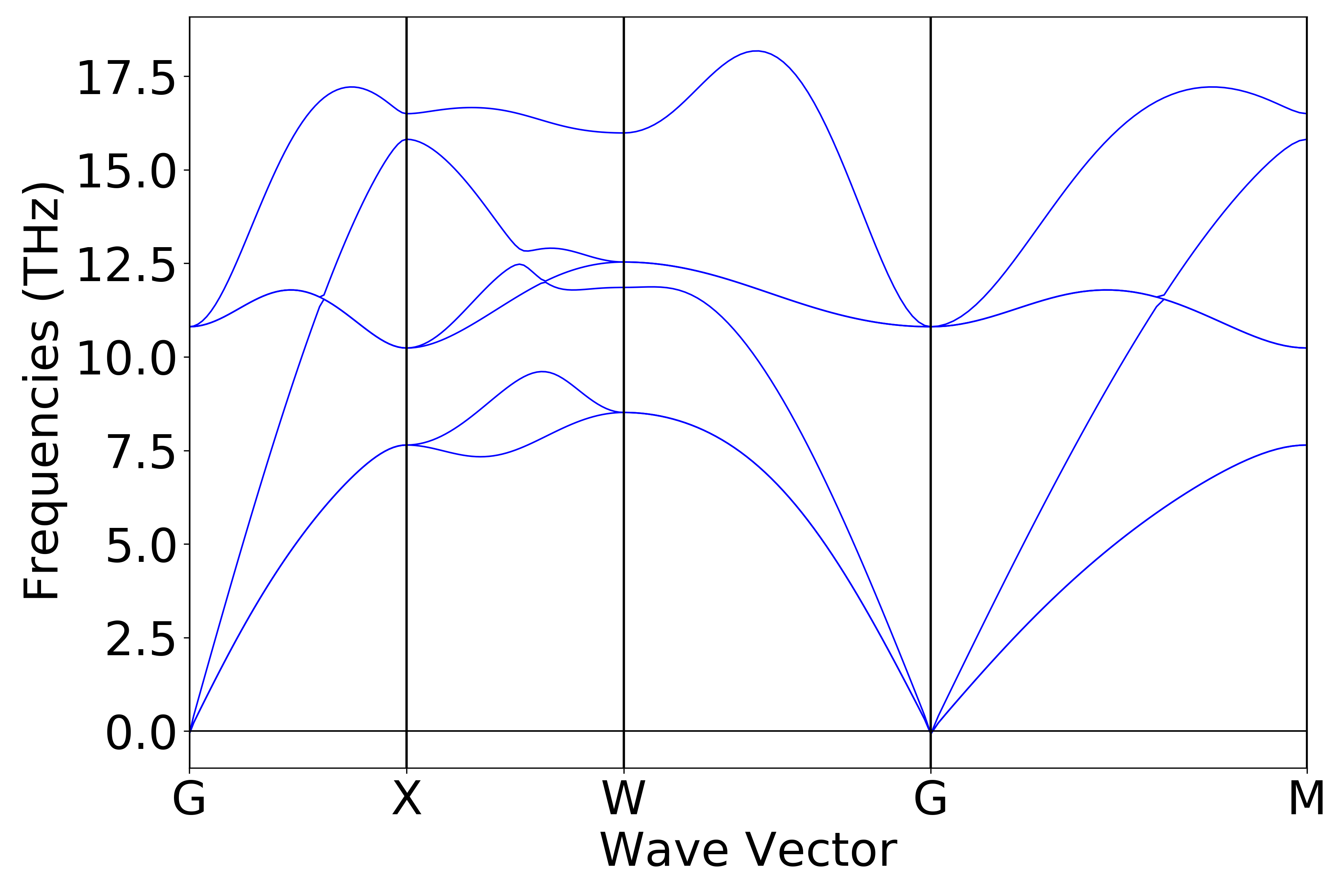
参考
9phonon_bandplot.py:
1# coding:utf-8
2import os
3
4from pymatgen.phonon.plotter import PhononBSPlotter
5
6from dspawpy.io.read import get_phonon_band_data
7
8band_data = get_phonon_band_data(
9 "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.16.1/phonon.h5",
10) # Read phonon band structure
11bsp = PhononBSPlotter(band_data)
12axes_or_plt = bsp.get_plot(ylim=None, units="thz") # Y-axis range # Units
13import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # noqa: E402
14
15if isinstance(axes_or_plt, plt.Axes):
16 fig = axes_or_plt.get_figure() # version newer than v2023.8.10
17elif isinstance(axes_or_plt, tuple):
18 fig = axes_or_plt[0].get_figure()
19else:
20 fig = axes_or_plt.gcf() # older version pymatgen
21
22filename = "dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/9phonon_bandplot.png" # File name for the output phonon band plot
23os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(filename)), exist_ok=True)
24fig.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
执行代码可以得到类似以下声子能带曲线:
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
声子态密度数据处理
参考
9phonon_dosplot.py:1# coding:utf-8 2import os 3 4from pymatgen.phonon.plotter import PhononDosPlotter 5 6from dspawpy.io.read import get_phonon_dos_data 7 8dos = get_phonon_dos_data("dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.16.1/phonon.h5") 9dp = PhononDosPlotter( 10 stack=False, # True indicates drawing an area plot 11 sigma=None, # Gaussian blur parameter 12) 13dp.add_dos( 14 label="Phonon", dos=dos 15) # Legend # The phonon density of states to be plotted 16axes_or_plt = dp.get_plot( 17 xlim=[0, 20], # x-axis range 18 ylim=None, # y-axis range 19 units="THz", # Unit 20) 21import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # noqa: E402 22 23if isinstance(axes_or_plt, plt.Axes): 24 fig = axes_or_plt.get_figure() # version newer than v2023.8.10 25elif isinstance(axes_or_plt, tuple): 26 fig = axes_or_plt[0].get_figure() 27else: 28 fig = axes_or_plt.gcf() # older version pymatgen 29 30filename = " dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/9phonon_dosplot.png" # Energy barrier plot output filename 31os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(filename)), exist_ok=True) 32fig.savefig(filename, dpi=300)
执行代码可以得到类似以下声子态密度曲线:
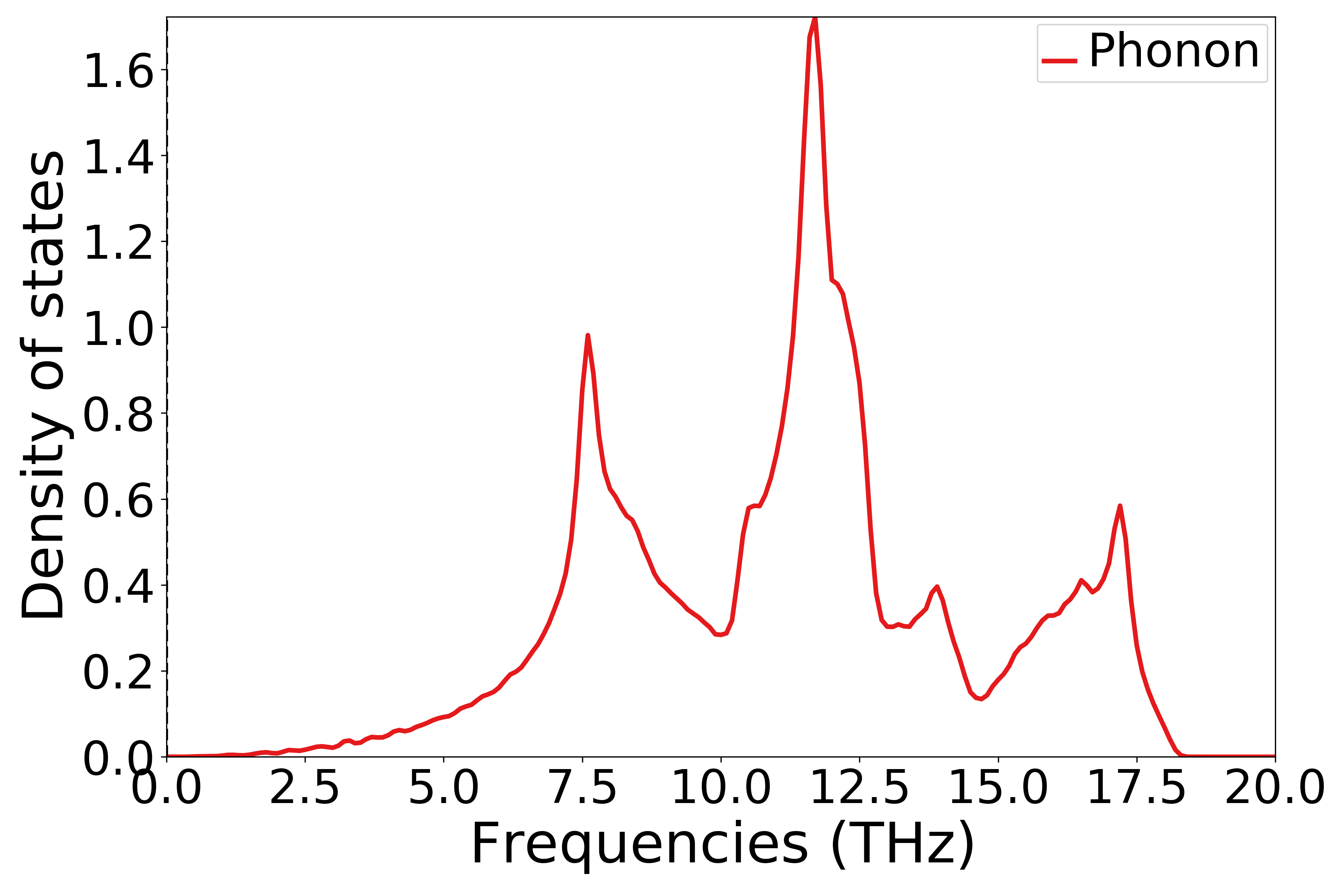
单晶硅声子态密度示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
声子热力学数据处理
可以参考 9phonon_thermal.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2from dspawpy.plot import plot_phonon_thermal
3
4plot_phonon_thermal(
5 datafile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.26/phonon.h5", # phonon.h5 data file path
6 figname="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/9phonon.png", # Output phonon thermodynamics figure filename
7 show=False, # Whether to display the image
8)
执行代码可以得到类似以下声子热力学曲线:

单晶硅声子热力学性质示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
8.10 aimd分子动力学模拟数据处理
以快速入门 \(H_{2}O\) 分子体系分子动力学模拟得到的 aimd.h5 为例:
轨迹文件转换格式为.xyz或.dump
从aimd输出的hdf5文件中读取数据,并生成轨迹文件
生成的.xyz或.dump格式文件,可拖入OVITO观察,通过 Device Studio --> Simulator --> OVITO 打开 OVITO 可视化界面,将xyz文件或dump文件拖入OVITO即可。
参考 10write_aimd_traj.py :
1# coding:utf-8
2from dspawpy.io.structure import convert
3
4convert(
5 infile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.18/aimd.h5", # Structure to be converted, if in the current path, only the filename can be written
6 si=None, # Filter the configuration number, if not specified, read all by default
7 ele=None, # Filter element symbol, default reads atomic information for all elements
8 ai=None, # Filter atomic indices (starting from 1), default to read all atomic information
9 outfile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/10aimdTraj.xyz", # Can also generate .dump files (lower precision), currently only supports orthogonal unit cells
10)
执行代码将生成.xyz和.dump格式的轨迹文件,该文件可通过OVITO打开。关于结构文件转化的更多细节,请参考 structure结构转化
知识点:
OVITO 与 dspawpy 都不支持将非正交晶胞的体系保存为dump文件
动力学过程中能量、温度等变化曲线
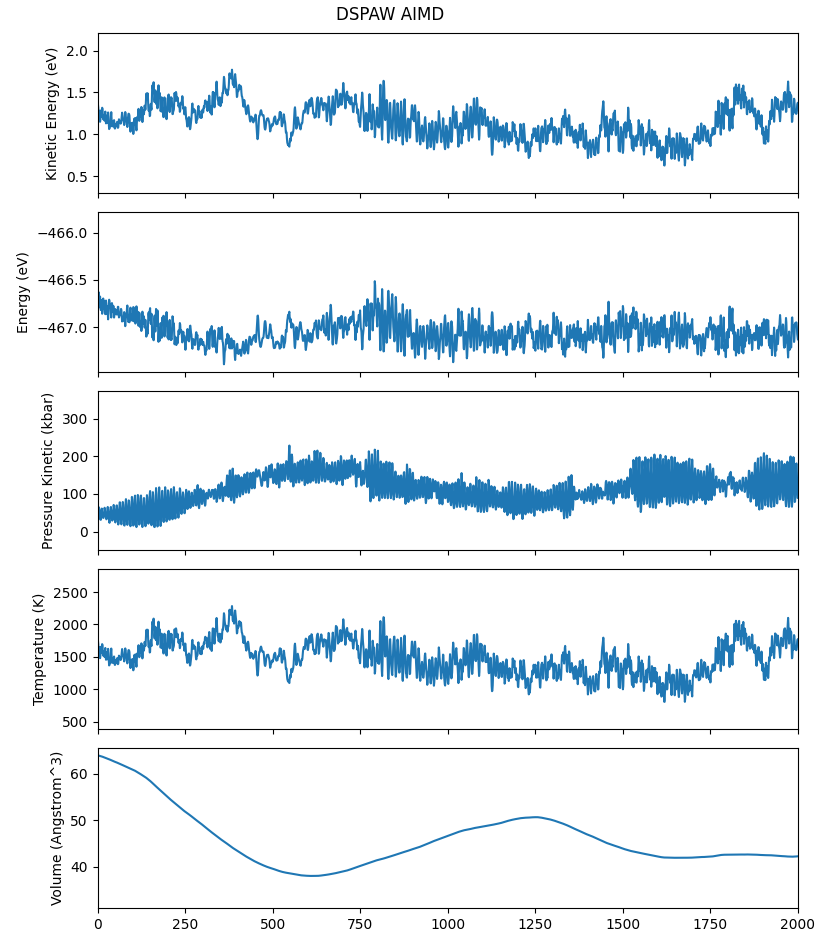
参考
10check_aimd_conv.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.plot import plot_aimd 3 4plot_aimd( 5 datafile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.18/aimd.h5", # Data file path 6 show=False, # Whether to pop up the image window 7 figname="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/10aimd.png", # Output image file name 8 flags_str="1 2 3 4 5", # Select data types 9) 10# The meaning of flags_str is as follows 11# 1. Kinetic energy 12# 2. Total Energy 13# 3. Pressure 14# 4. Temperature 15# 5. Volume
执行代码将生成如下组合图:
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
均方位移(MSD) 分析
参考
10aimd_msd.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.analysis.aimdtools import get_lagtime_msd, plot_msd 3 4# If AIMD is not completed in one go, you can assign multiple h5 file paths to the datafile parameter in a list form 5lagtime, msd = get_lagtime_msd( 6 datafile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.18/aimd.h5", # Data file path 7 select="all", # Default selects all atoms 8 msd_type="xyz", # Default to calculate MSD in the xyz directions 9 timestep=None, # Default reads the timestep from the datafile 10) 11# Plot the graph using the obtained data and save it 12plot_msd( 13 lagtime, # X-axis coordinate 14 msd, # vertical axis 15 xlim=None, # Set the display range of the x-axis 16 ylim=None, # Set the display range of the y-axis 17 figname="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/10MSD.png", # Output image filename 18 show=False, # Whether to pop up the image window 19 ax=None, # Optional subplot specification 20)
执行代码将生成类似如下图片:
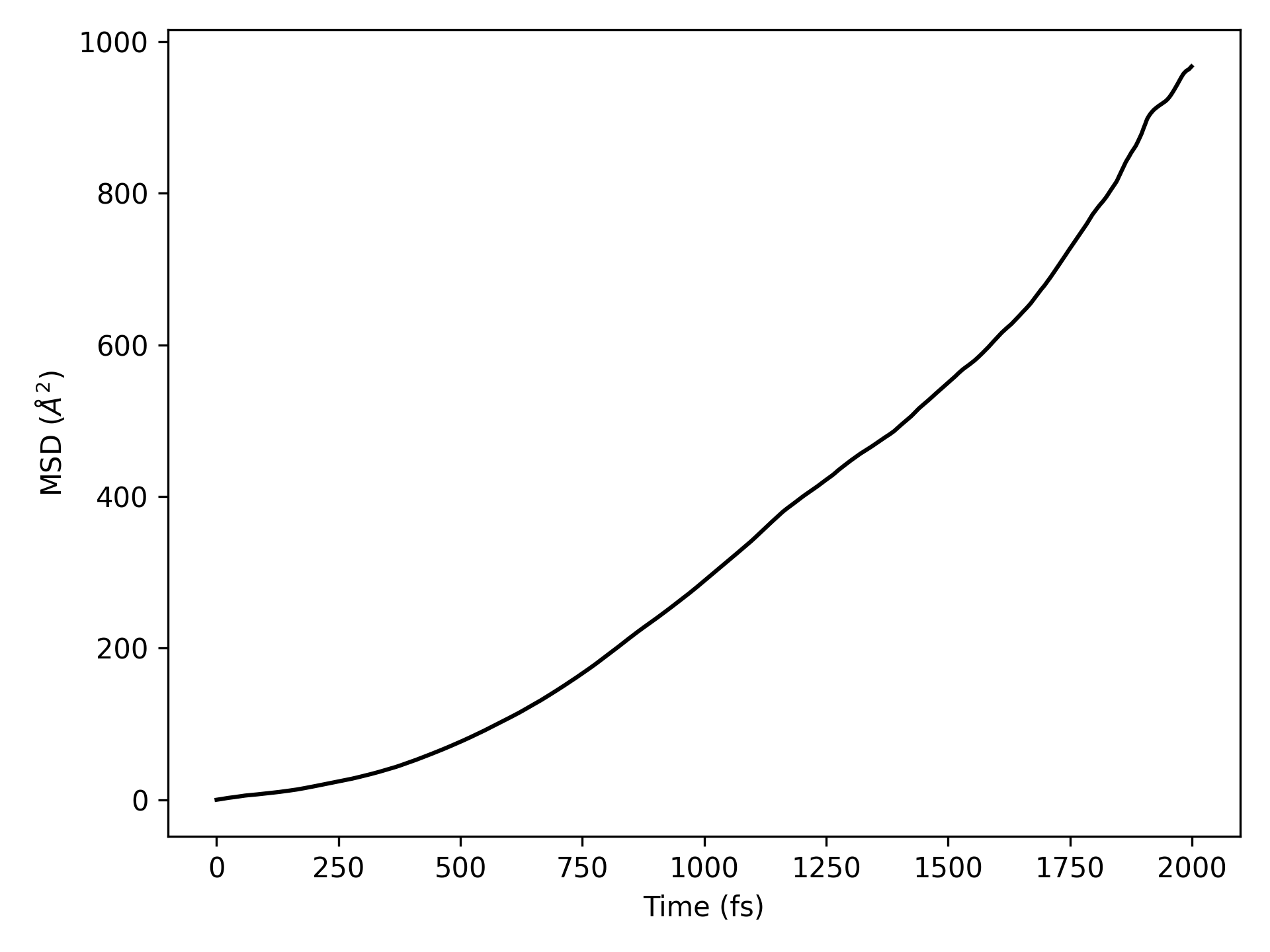
均方位移(MSD)示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
均方根偏差(RMSD) 分析
参考
10aimd_rmsd.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.analysis.aimdtools import get_lagtime_rmsd, plot_rmsd 3 4# If AIMD is not completed in a single run, you can assign multiple paths of h5 files in list form to the datafile parameter 5lagtime, rmsd = get_lagtime_rmsd( 6 datafile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.18/aimd.h5", 7 timestep=None, # Data file path # Default reads the time step from the datafile 8) 9plot_rmsd( 10 lagtime, # Horizontal coordinate 11 rmsd, # vertical coordinate 12 xlim=None, # Set the display range of the x-axis 13 ylim=None, # Set the display range of the y-axis 14 figname="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/10RMSD.png", # Output image filename 15 show=False, # Whether to pop up the image window 16 ax=None, # Optional subplot specification 17)
执行代码将生成类似如下图片:
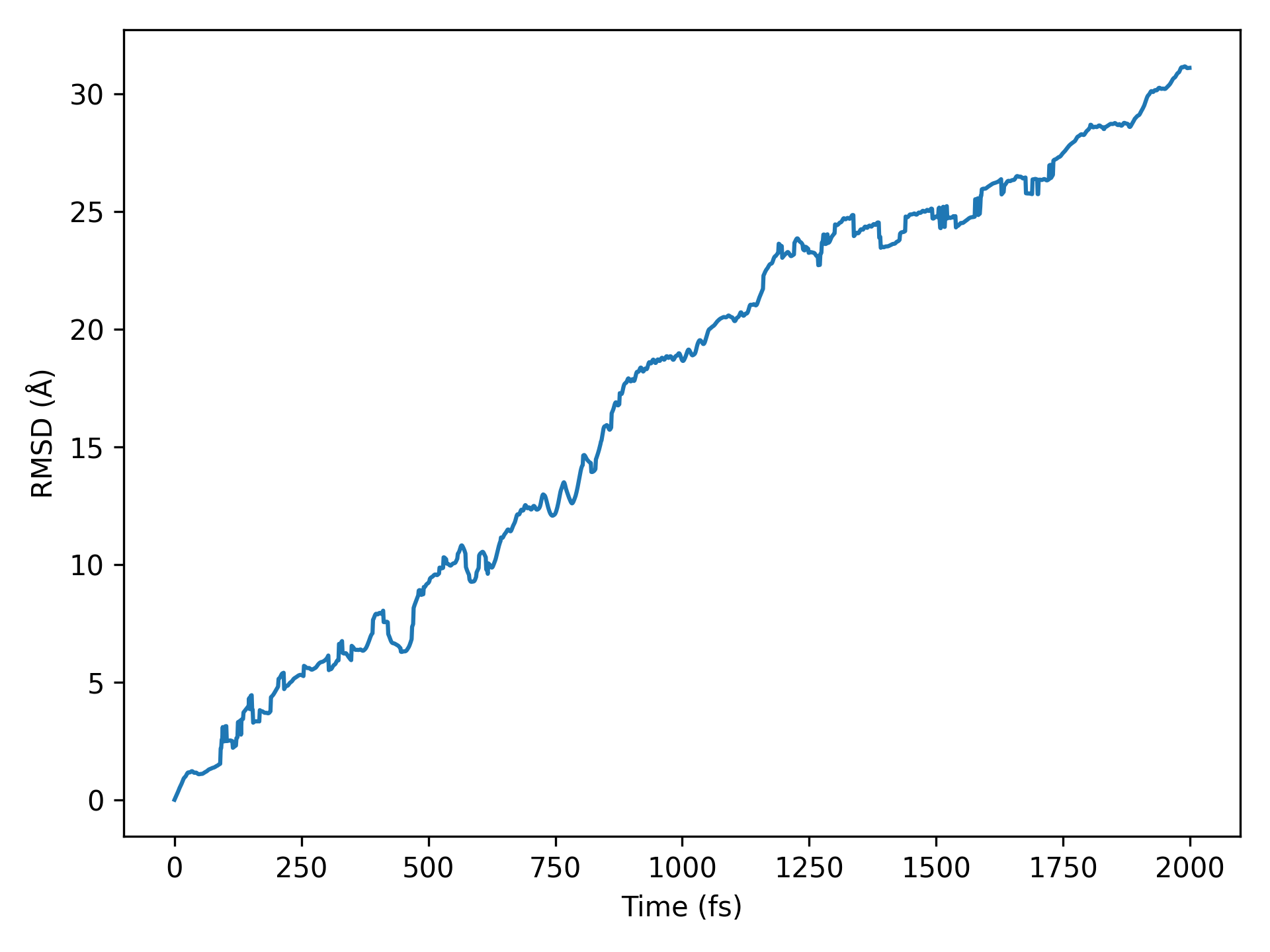
均方根偏差(RMSD)示意图
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
原子对分布函数或径向分布函数(RDFs) 分析
参考
10aimd_rdf.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.analysis.aimdtools import get_rs_rdfs, plot_rdf 3 4# If AIMD is not completed in one go, you can assign multiple h5 file paths to the datafile parameter in the form of a list. 5rs, rdfs = get_rs_rdfs( 6 datafile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.18/aimd.h5", # Data file path 7 ele1="H", # Central element 8 ele2="O", # Target element 9 rmin=0.0, # Minimum radius 10 rmax=10.0, # Maximum radius 11 ngrid=1000, # Number of grid points 12 sigma=0.1, # sigma value 13) 14plot_rdf( 15 rs, # x-axis values 16 rdfs, # Vertical coordinate 17 "H", # Central element 18 "O", # Object element 19 figname="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/10RDF.png", # Image save path 20 show=False, # Whether to pop up the image window 21 ax=None, # Subplot can be specified 22)
执行代码将生成类似如下图片:
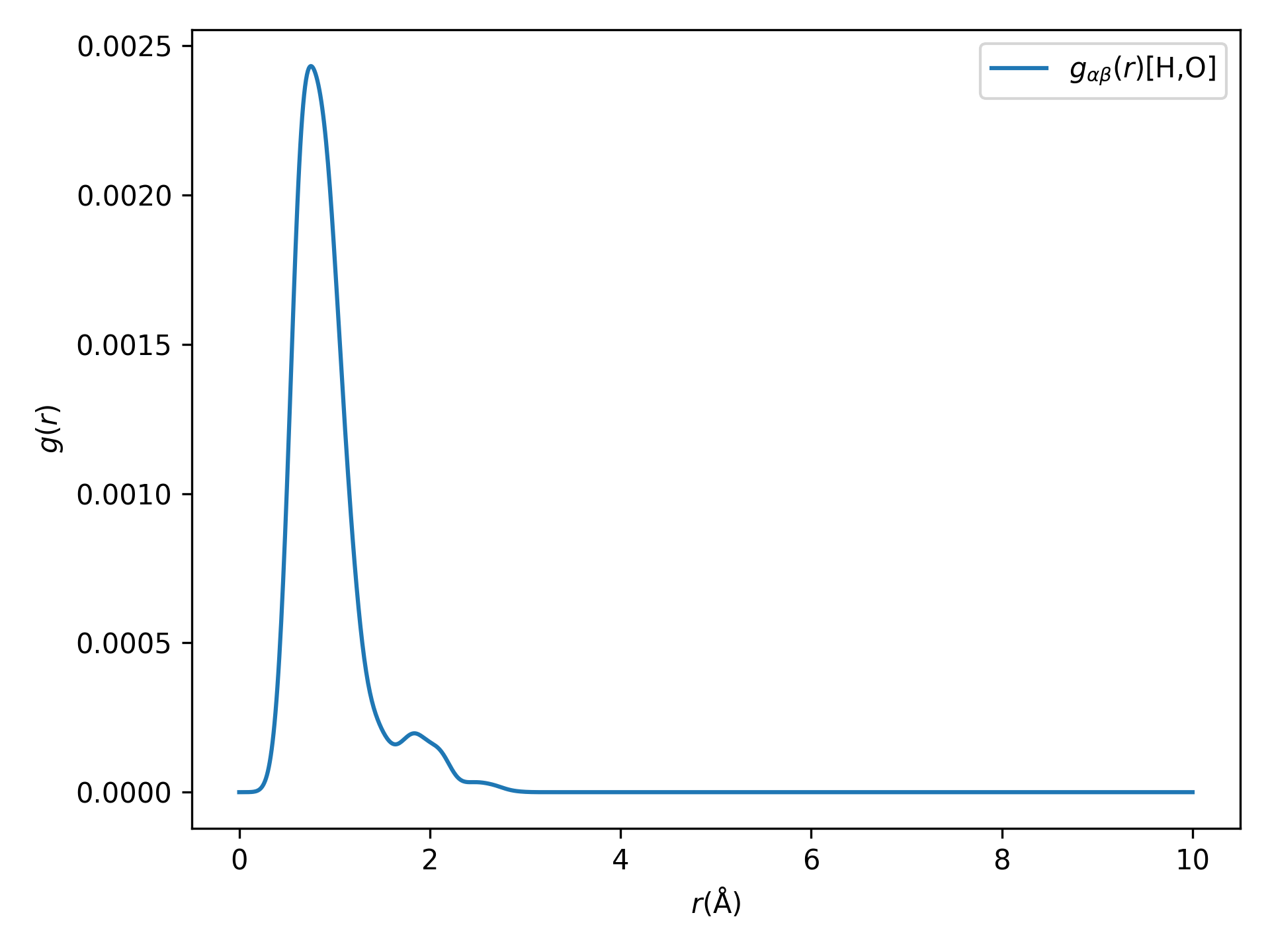
径向分布函数(RDFs)示意图
这部分涉及的统计学计算较复杂,更多细节请参考函数API
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
8.11 Polarization铁电极化数据处理
以快速入门 \(HfO_{2}\) 体系铁电计算得到的系列 scf.h5 为例:
参考
11Ferri.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.plot import plot_polarization_figure 3 4plot_polarization_figure( 5 directory="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.20", # Path for iron polarization calculation 6 repetition=2, # Number of times to repeat the data points when plotting 7 figname="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/outputs/us/11pol.png", # Output polarization figure filename 8 show=False, # Whether to display the polarization figure 9) # --> pol.png
执行代码将生成如下组合图:
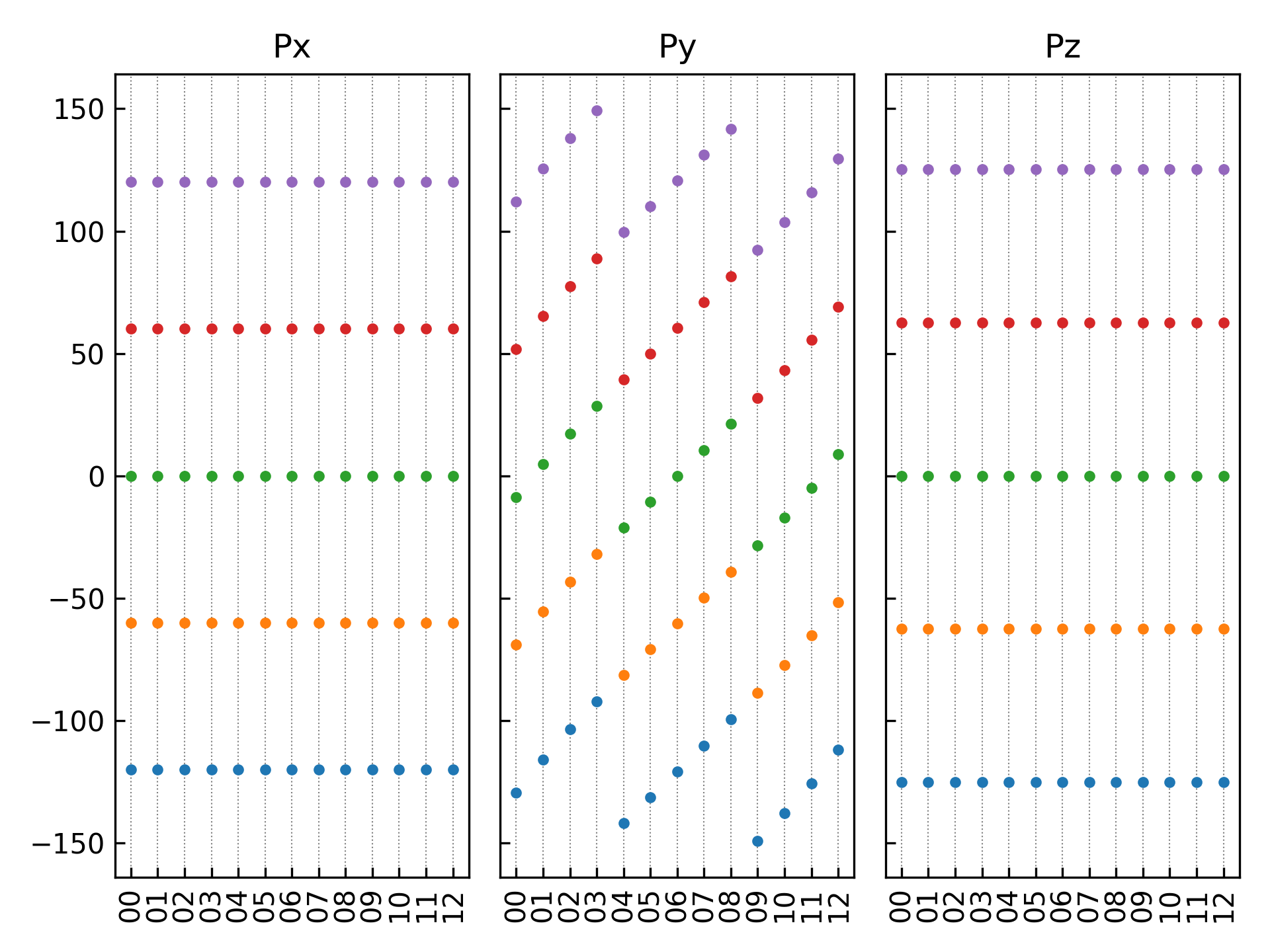
12组结构对应极化数值
查看首尾构型的铁电极化数值,可以参考如下:
1from dspawpy.plot import plot_polarization_figure 2 3plot_polarization_figure(directory='.', annotation=True, annotation_style=1) # 显示首尾构型的铁电极化数值
执行代码将生成如下组合图:
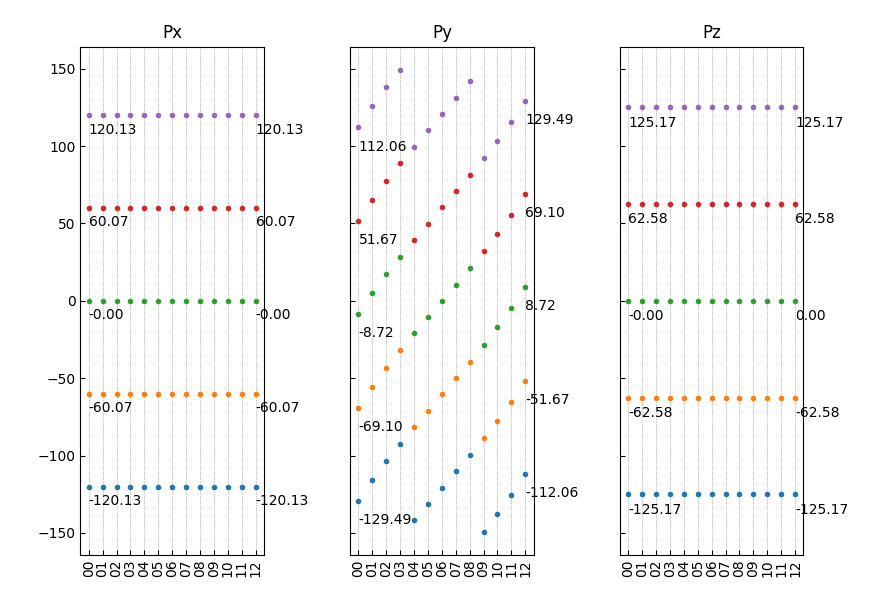
12组结构对应极化数值(带首尾构型数值)
也可以使用第二种批注样式:
1from dspawpy.plot import plot_polarization_figure 2 3plot_polarization_figure(directory='.', annotation=True, annotation_style=2) # 显示首尾构型的铁电极化数值
执行代码将生成如下组合图:
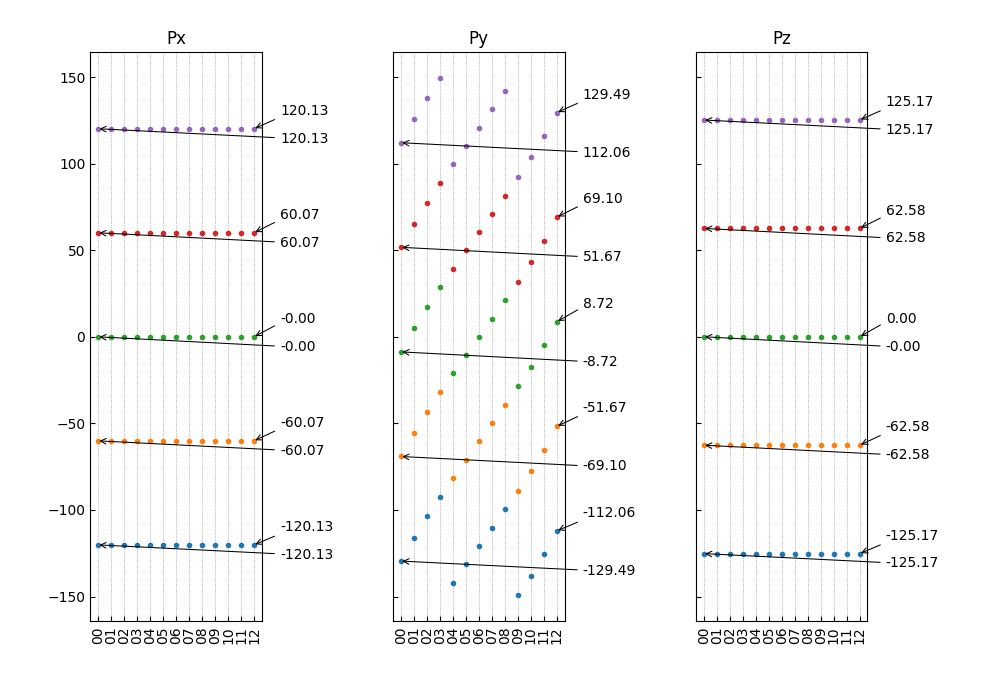
12组结构对应极化数值(带首尾构型数值)
警告
如果通过SSH连接到远程服务器执行上述脚本,出现QT相关的报错信息,可能是使用的程序(比如MobaXterm等)和QT库不兼容,要么更换程序(例如VSCode或者系统自带的终端命令行),要么请在python脚本第二行开始添加以下代码:
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('agg')
8.12 ZPE零点振动能数据处理
以快速入门 \(CO\) 体系频率计算得到的 frequency.txt 文件为例,计算零点振动能,基于以下公式:
其中, \(\nu_i\) 是简正频率, \(h\) 是普朗克常数( \(6.626\times10^{-34} J\cdot s\)), \(N\) 是原子数。
参考
12getZPE.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.io.utils import getZPE 3 4# Import the frequency.txt file obtained from frequency calculation 5getZPE( 6 fretxt="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.13/frequency.txt", 7)
执行代码结果文件将保存到 ZPE.dat 文件中,文件内容如下:
Data read from D:\quickstart\2.13\frequency.txt Frequency (meV) 284.840038 --> Zero-point energy, ZPE (eV): 0.142420019
8.13 TS的热校正能
吸附质的熵变对能量的贡献
计算基于以下公式:
其中, \(\Delta S_{a d s}\) 表示吸附质的熵变,根据简谐近似计算。\(S_{v i b}\) 表示振动熵。 \(\nu_i\) 是简正频率,\(N_A\) 是阿伏伽德罗常数( \(6.022\times10^{23} mol^{-1}\) ), \(h\) 是普朗克常数( \(6.626\times10^{-34} J\cdot s\)), \(k_B\) 是玻尔兹曼常数( \(1.38\times10^{-23} J\cdot K^{-1}\)), \(R\) 是理想气体常数( \(8.314 J\cdot mol^{-1}\cdot K^{-1}\)), \(T\) 是体系温度,单位 \(K\)。
参考
13getTSads.py:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.io.utils import getTSads 3 4# Import the frequency.txt file calculated from frequency, temperature can be modified arbitrarily 5getTSads( 6 fretxt="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.13/frequency.txt", 7 T=298.15, 8)
执行代码结果文件将保存到 TS.dat 文件中,文件内容如下:
Data read from D:\quickstart\2.13\frequency.txt Frequency (THz) 68.873994 --> Entropy contribution, T*S (eV): 4.7566990201851275e-06
理想气体的熵变对能量的贡献
计算基于如下公式:
其中:
其中:\(I_A\) 到 \(I_C\) 是非线性分子的三个主惯性矩, \(I\) 是线性分子的简并惯性矩, \(\sigma\) 是分子的对称数。另外,monatomic 表示单原子分子,linear 表示线性分子,nonlinear 表示非线性分子。total spin 是总自旋数。 vib DOF 表示振动自由度。
参考
13getTSgas.py脚本处理:1# coding:utf-8 2from dspawpy.io.utils import getTSgas 3 4# Read elements and coordinates from the calculation result file (json or h5) 5TSgas = getTSgas( 6 fretxt="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.13/frequency.txt", 7 datafile="dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.13/frequency.h5", 8 potentialenergy=-0.0, 9 geometry="linear", 10 symmetrynumber=1, 11 spin=1, 12 temperature=298.15, 13 pressure=101325.0, 14) 15print("Entropy contribution, T*S (eV):", TSgas) 16 17# If only the frequency.txt file is available, the calculation can be completed by manually specifying the elements and coordinates 18# TSgas = getTSgas(fretxt='dspawpy_proj/dspawpy_tests/inputs/2.13/frequency.txt', datafile=None, potentialenergy=-0.0, elements=['H', 'H'], geometry='linear', positions=[[0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0]], symmetrynumber=1, spin=1, temperature=298.15, pressure=101325.0)
8.14 附录
快速下载所有脚本,点击
用户脚本.zip